报告题目:Adding Environmental Sustainability to Biomass Valorization
报告人:Joseph Samec教授
邀请人:李雪辉教授
报告时间:2024年6月28日上午10:30~12:00
报告地点:制浆造纸工程国家重点实验室D楼306会议室
欢迎广大师生踊跃参加!
制浆造纸工程国家重点实验室
轻工科学与工程学院
2024年6月24日
报告摘要:
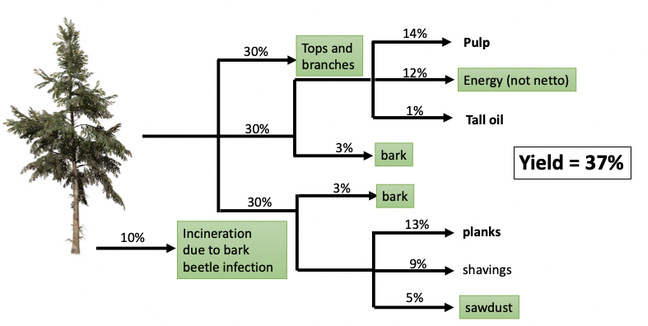
In only 40 years from now, our demand based on population will increase by 25% while our main source of materials and energy will be exhausted. Thus, our society is facing major counteracting challenges where our demand will increase while our supplies decrease. When addressing these challenges, care must be taken to mitigate resource depletion, climate change, land use and other environmental impact categories. Biomass will play a major role as a resource for chemicals, materials and even fuels. However, using biomass is not necessarily sustainable; care must be taken specially to mitigate burden on resource depletion, irrigation, and land use. In fact, current forestry is rather inefficient where yield of high value products is below 40%. One strategy is to use streams of biomass that currently are burnt to a low value, where burning biomass can be considered carbon neutral but not necessarily climate neutral. In this talk, strategies and examples on valorizing side-streams from Nordic forestry will be given. This will include upgrading of black liquor from pulp industries, tops and branches and insect killed forestry residues, and bark.
References:
Sustainable Aviation Fuel from Prehydrolysis Liquors Green Chemistry 2024, 27 DOI: 10.1039/d4gc01257g
Valorization of Tops and Branches to Textile Fibers and Biofuel: Value Chain Explored Experimentally; Environmental Sustainability Evaluated by Life Cycle Assessment ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12, 526-533
Valorization of beetle infected spruce to produce textile fibers and biofuels: Environmental sustainability evaluated by life cycle assessment Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 144179
Lignin-first biorefining of Nordic poplar to produce cellulose fibers could displace cotton production on agricultural lands Joule 2022, 6, 1845–1858.
De‐bottlenecking a pulp mill by producing biofuels from black liquor in 3 steps, ChemSusChem, 2021, 14, 2414-2425
报告人简介:
Joseph Samec received his Ph.D. from the University of Stockholm, Sweden, in 2005 with Prof. Bäckvall as supervisor. After a postdoctoral training with Prof. Grubbs at CalTech, USA, during 2006–2007, he was appointed as Assistant Professor at University of Uppsala in Sweden. In 2015 he moved to Stockholm University where he is currently professor. His research interests focus on green chemistry in organic synthesis and biomass processing and applications. In 2012, he founded RenFuel, a start-up company that is producing biofuels from lignin; and then 2015 RenCom and 2018 LigniCore that produce materials from lignin.