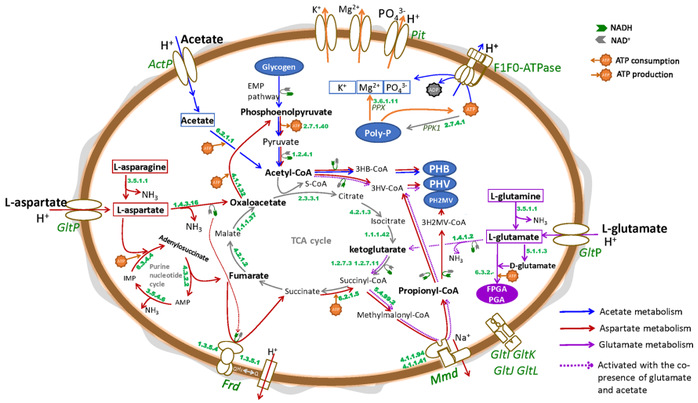
A/Prof Qiu Guanglei and their co-workers have proposed a method for direct phosphorus removal and recovery from municipal wastewater via forward osmosis membrane bioreactor (FOMBR). A hybrid microfiltration -forward osmosis membrane bioreactor was subsequently developed for salt accumulation control and facilitated phosphorus recovery (Environ Sci Technol, 2015, 49, 6156-6163). The concept of contaminates retention time (CRT) was proposed with a disclosure of the decoupling of contaminates retention time (CRT) and hydraulic retention time (HRT) in the FOMBR process (Water Res, 2016, 105, 370-382). The unparalleled new feature allowed a reduction of the HRT for biological wastewater treatment to sub-hour level, achieving increases in the wastewater treatment and phosphorus recovery capacities by an order of a magnitude. He and his co-workers also revealed the governing role of electrostatic interaction in the bi-directional transport of electrolyte in the FO process (Water Res, 2020, 173, 115590). In the area of enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR), A/Prof. Qiu and co-workers have showed the ability of polyphosphate accumulating organisms in full-scale wastewater treatment to use diverse carbon sources (Water Res, 149, 2019, 496-510). Subsequent research allowed the discovery of the ability of Ca. Accumulibacter to use amino acids as carbon sources for EBPR, the respective metabolic pathways was re-constructed via combined biochemical and meta-omics characterization (Environ Sci Technol, 2020, 54, 2448−2458). These works substantially improved our understanding on the EBPR process.