科研动态
- 孔宪教授课题组本科生独立工作发表在Mol. Syst. Des. Eng.:电荷监督的等变架构实现数据高效的分子性质预测 02-04
- 华南理工大学孔宪教授团队 《Small》:不对称表面电荷修饰调控受限聚合物电解质中的溶剂化结构和离子电导率 01-28
- 华南理工王宇团队JACS: AI赋能确立“催组装三要素”新原理,开辟手性材料智能创制新范式 12-25
- 华南理工王辉副教授 Nature Communications :靶向线粒体的自发光氟化高分子纳米粒动脉粥样硬化治疗! 11-10
- 华南理工孔宪教授 AFM:PEO基聚合物电解质中氟化模式对溶剂化和离子传输性质的调控 11-10
- 华南理工科研人员合作成果,在Nature发表! 11-03
A Transparent, Highly Stretchable, Solvent-Resistant, Recyclable Multifunctional Ionogel with Underwater Self-Healing and Adhesion for Reliable Strain Sensors
Liguo Xu,Zhenkai Huang,Zhishuang Deng,Zhukang Du,Tao Lin Sun,Zi-Hao Guo,Kan Yue*
Advanced Materials,2021,DOI:10.1002/adma.202105306
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202105306
Abstract
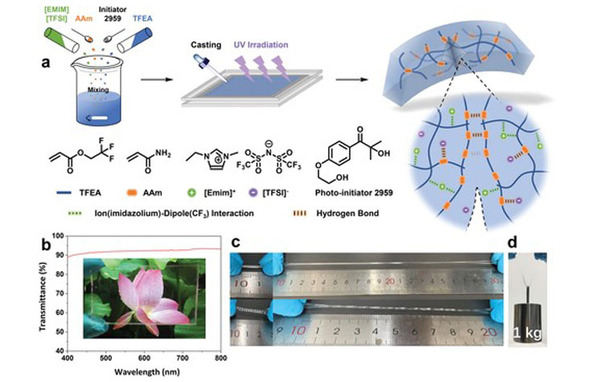
Ionogels have gained increasing attentions as a flexible conductive material. However, it remains a big challenge to integrate multiple functions into one gel that can be widely applied in various complex scenes. Herein, a kind of multifunctional ionogels with a combination of desirable properties, including transparency, high stretchability, solvent and temperature resistance, recyclability, high conductivity, underwater self-healing ability, and underwater adhesiveness is reported. The ionogels are prepared via one-step photoinitiated polymerization of 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl acrylate and acrylamide in a hydrophobic ionic liquid. The abundant noncovalent interactions including hydrogen bonding and ion–dipole interactions endow the ionogels with excellent mechanical strength, resilience, and rapid self-healing capability at room temperature, while the fluorine-rich polymeric matrix brings in high tolerance against water and various organic solvents, as well as tough underwater adhesion on different substrates. Wearable strain sensors based on the ionogels can sensitively detect and differentiate large body motions, such as bending of limbs, walking and jumping, as well as subtle muscle movements, such as pronunciation and pulse. It is believed that the designed ionogels will show great promises in wearable devices and ionotronics.



