科研动态
- 孔宪教授课题组本科生独立工作发表在Mol. Syst. Des. Eng.:电荷监督的等变架构实现数据高效的分子性质预测 02-04
- 华南理工大学孔宪教授团队 《Small》:不对称表面电荷修饰调控受限聚合物电解质中的溶剂化结构和离子电导率 01-28
- 华南理工王宇团队JACS: AI赋能确立“催组装三要素”新原理,开辟手性材料智能创制新范式 12-25
- 华南理工王辉副教授 Nature Communications :靶向线粒体的自发光氟化高分子纳米粒动脉粥样硬化治疗! 11-10
- 华南理工孔宪教授 AFM:PEO基聚合物电解质中氟化模式对溶剂化和离子传输性质的调控 11-10
- 华南理工科研人员合作成果,在Nature发表! 11-03
Extreme modulation of liquid crystal viscoelasticity via altering the ester bond direction
Wentao Tang, Minghui Deng, Junichi Kougo, Li Ding, Xiuhu Zhao, Yuki Arakawa*, Kenta Komatsu, Hideto Tsuji, Satoshi Aya*
J. Mater. Chem. C. 9, 9990-9996(2021)
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TC01636A
Abstract
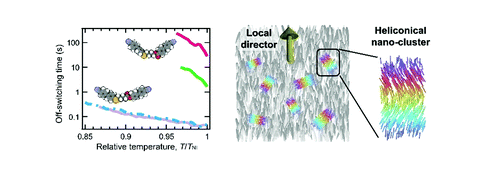
The understanding of correlations between molecular details and macroscopic material behavior is a fundamental question of molecular chemistry/physics and offers practical interest in materials design with fine-property-tunability. Herein, we demonstrate extreme modulation of liquid crystal (LC) viscoelasticity triggered by a reversion of the ester bond direction in two series of sulfur-containing cyanobiphenyl-based LC dimers. They possess two oppositely directed ester linkages (i.e., C=OO or OC=O), namely COOn and OCOn, respectively, and different carbon atom numbers of the short alkylene spacers (n = 4 and 6). Unexpectedly, it has been proven that the COOn homologs exhibit extraordinarily enhanced viscoelastic properties in the fluidic nematic (N) phase (up to about 1000 times) compared with their OCOn counterparts. Besides, dielectric spectroscopy revealed that the degree of the collective orientational fluctuation is significantly affected by reversing the ester bond direction, suggesting the existence of heliconical clusters embedded in the N state. Finally, we have proposed a novel eco-driving LC memory device based on a pulse-electric-field driving method using COO4 with an extremely high rotational viscosity.
论文链接:
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/TC/D1TC01636A



