罗晓春教授课题组在生物降解领域取得系列新进展
生物降解是绿色循环经济的重要手段,可以帮助人类处理不同的生物质及废弃物。罗晓春教授近期在该方向取得了系列的进展,相关成果《Chitinases are important virulence factors in Vibrio for degrading the chitin-rich barrier of shrimp》[1]、《Sustainable valorizing high-protein feather waste utilization through solid-state fermentation by keratinase-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3 using a novel promoter》[2]、《Identification of a Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3 aminopeptidase SsLap1 and its synergistic with endopeptidase Sep39 for peanut meal hydrolysis》[3]、《Highly efficient and sustainable bioconversion of cottonseed meal to high-value products through solid-state fermentation by protease-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3》[4]、《Biodegradation of skatole by Bacillus subtilis GDAAS-A32 and its inhibition for odor emissions from swine manure》[5]、《Nutritional value improvement of soybean meal through solid-state fermentation by proteases-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3》[6]、《Bioconversion of agriculture by-products with functionally enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3: Fish skin as a model》[7],分别发表在《International Journal of Biological Macromolecules》(Q1,IF 8.5)、《Waste Management》(Q1,IF 7.1)、《Food Bioscience》(Q1,IF 5.9)、《Chemical Engineering Journal》(Q1,IF 13.2)、《Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering》(Q1,IF 7.2)、《International Journal of Biological Macromolecules》(Q1,IF 8.5)和《Food Chemistry》(Q1,IF 9.8)期刊,第一作者分别为博士生邓俊劲、硕士生陆雯珺、蔡华红、戴振杰、胡婧怡、博士生陆德林和硕士生倪静涛。
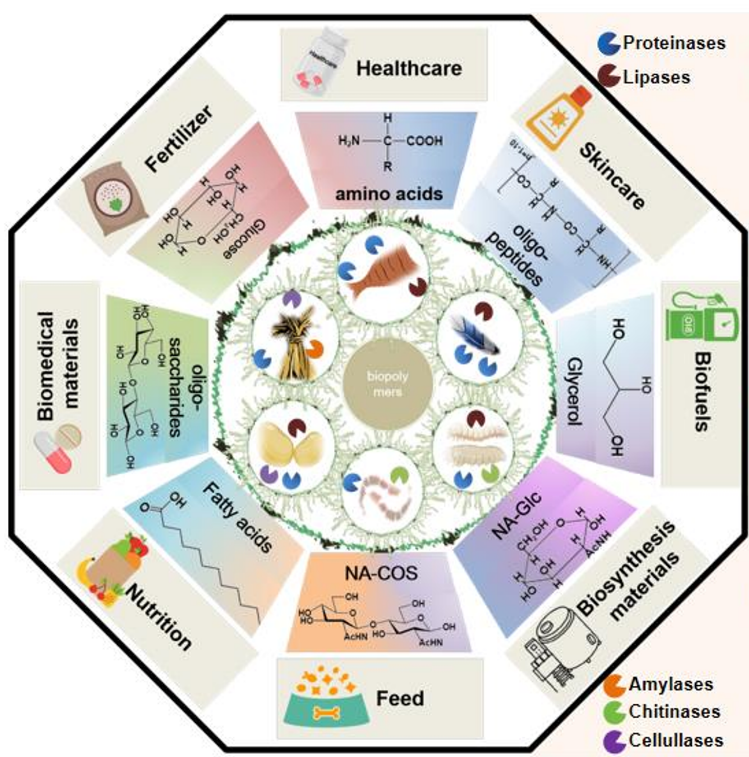
课题组通过解析天然微生物对生物大分子的降解机制,道法自然,通过合成生物学改造,加速了自然界中的降解过程。相关技术实现了蛋白(羽毛角蛋白、鱼皮胶原蛋白、植物蛋白等)、多糖(木质纤维素、几丁质、藻类多糖等)、油脂(动物内脏、厨余黑水虻)等生物质的快速降解,转化为人类能利用的寡聚体或者单体并高值化利用。
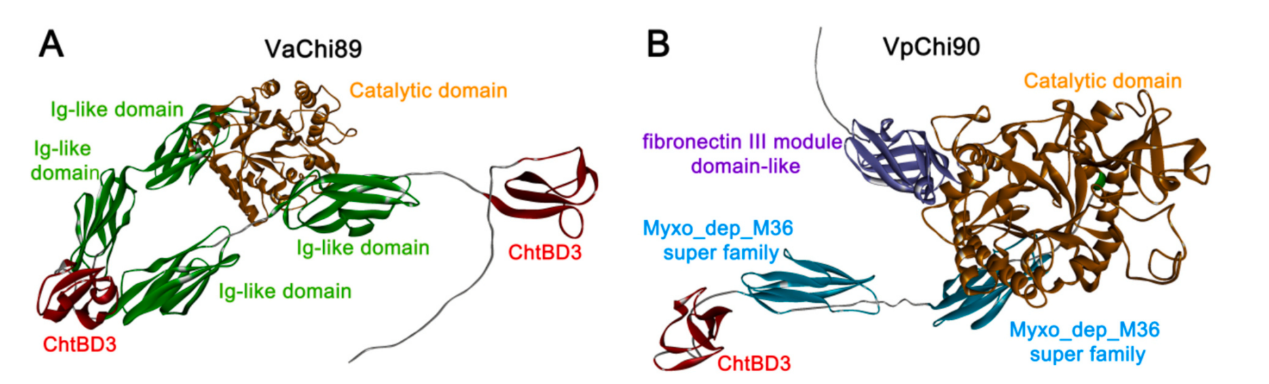
《Chitinases are important virulence factors in Vibrio for degrading the chitin-rich barrier of shrimp》一文介绍了弧菌的几丁质酶。弧菌是海洋的主要几丁质降解者,几丁质酶是一些条件致病菌入侵甲壳类的主要毒力因子。相关酶对甲壳素生物质的利用提供了有效的遗传元件。
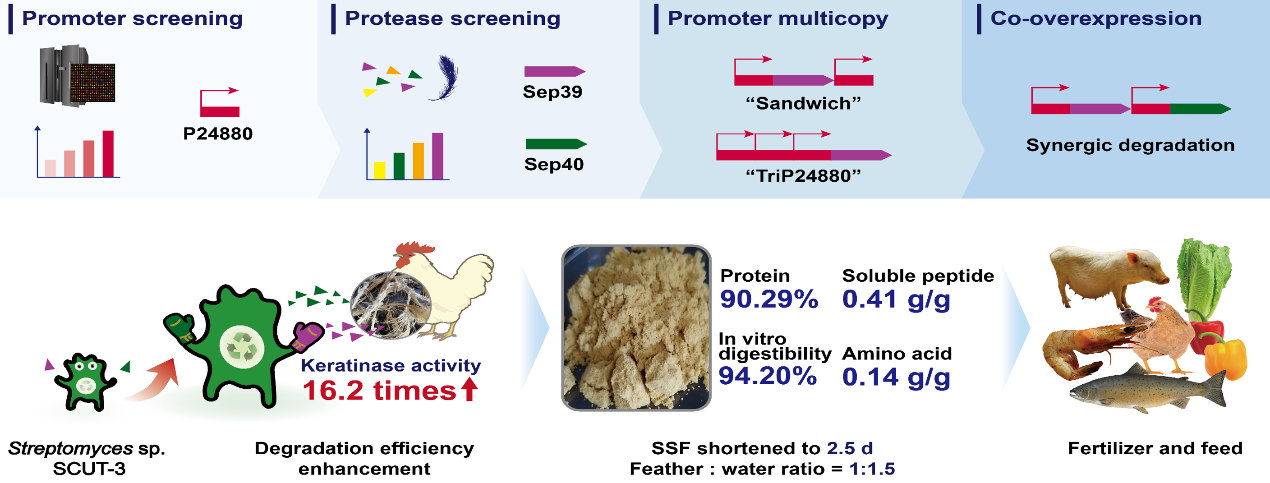
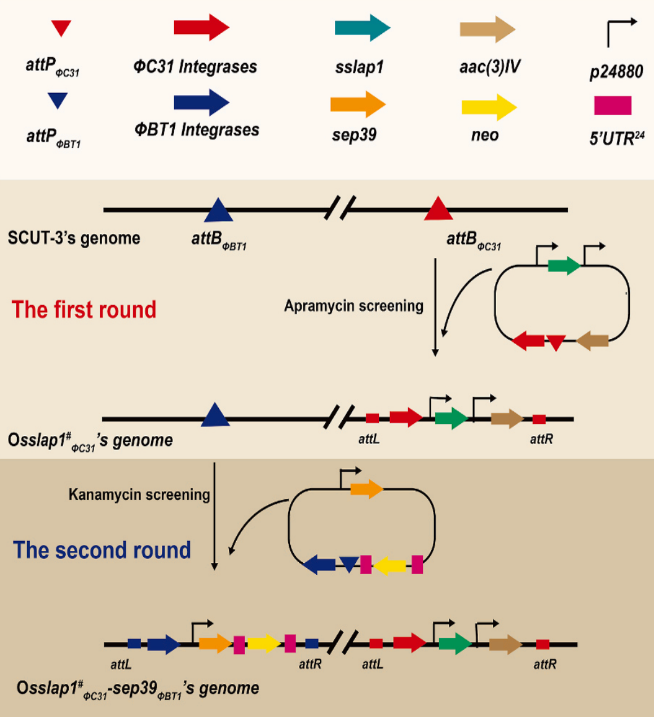
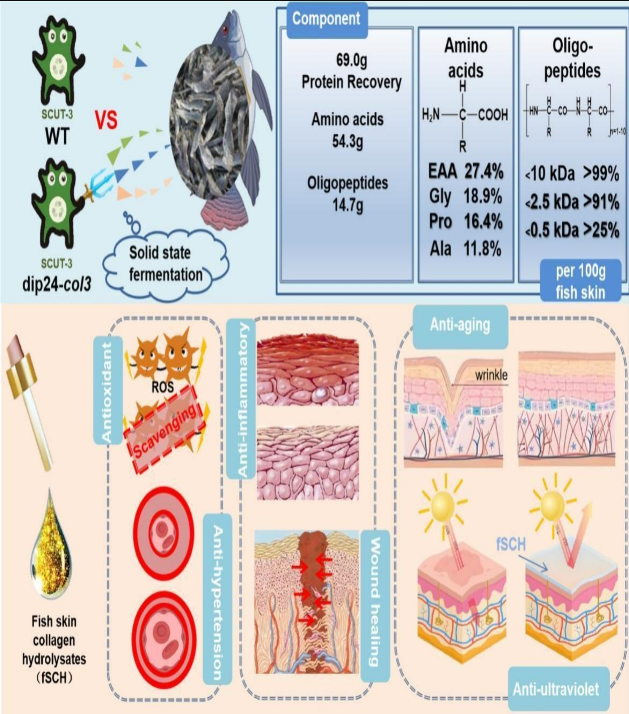
《Sustainable valorizing high-protein feather waste utilization through solid-state fermentation by keratinase-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3 using a novel promoter》一文,基于前期揭示的链霉菌SCUT-3羽毛二硫键还原及角蛋白降解的机制,通过强化重要角蛋白酶Sep39、Sep40的表达(利用新型启动子),成功将角蛋白酶活性提高了16.2倍,实现了羽毛固态发酵高效降解。《Identification of a Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3 aminopeptidase SsLap1 and its synergistic with endopeptidase Sep39 for peanut meal hydrolysis》一文通过二轮整合,实现了SCUT-3的亮氨酸氨肽酶SsLap1与其内肽酶Sep39的共过表达改造,相关酶对花生粕的蛋白降解显著增强,并可获得更多的游离氨基酸。该亮氨酸氨肽酶在切除肽段末端疏水氨基酸中效果明显,可用于水解多肽疏水氨基酸暴露后的苦味脱除。《Bioconversion of agriculture by-products with functionally enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3: Fish skin as a model》一文通过外源胶原蛋白酶在SCUT-3中的增强表达,实现了SCUT-3固态发酵对鱼皮胶原蛋白的高效降解,获得小分子的胶原肽及游离氨基酸,相关产物能有效促进人类皮肤细胞生长,具有抗衰、抗紫外、抗氧化等优良性能,可广泛添加于化妆品及口服胶原产品中。

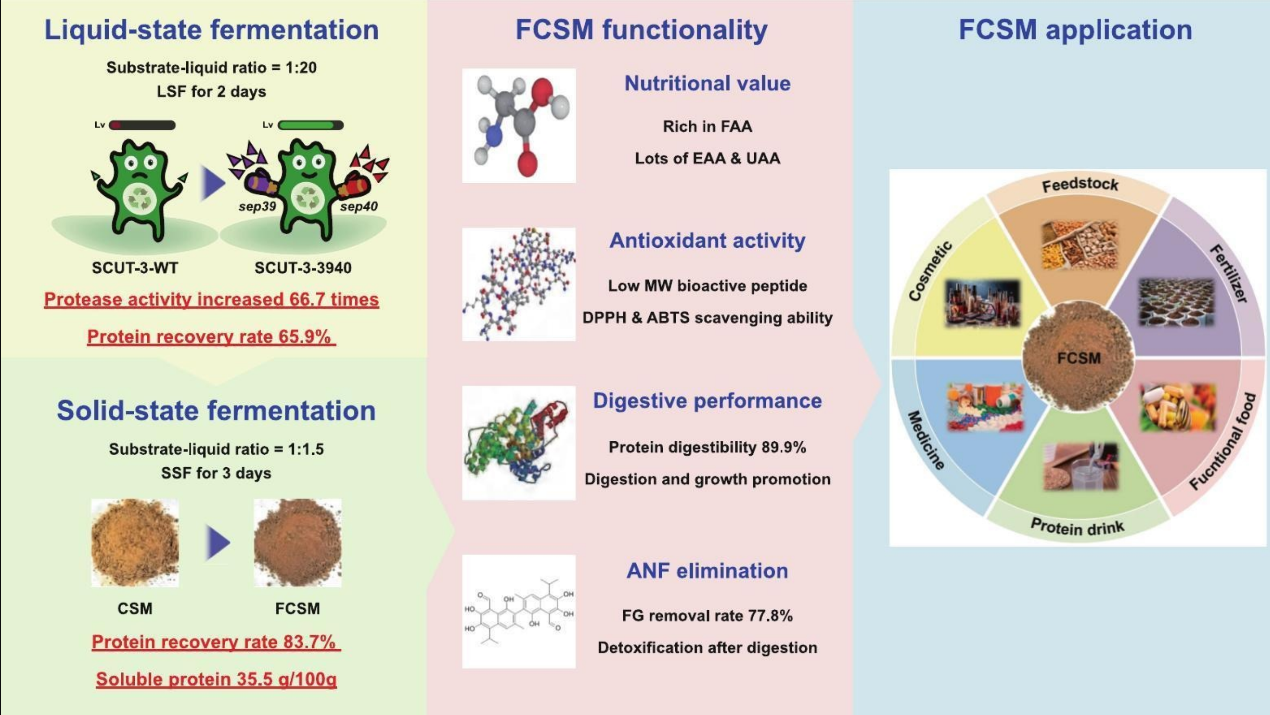
相关改造菌株在其它植物蛋白降解中也表现出相当好的性能。《Nutritional value improvement of soybean meal through solid-state fermentation by proteases-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3》一文用蛋白酶增强的SCUT-3菌株实现了豆粕的高效固态发酵,将其中的超过90%蛋白的蛋白回收成氨基酸、小肽,大大改善了大豆蛋白的可消化吸收率。《Highly efficient and sustainable bioconversion of cottonseed meal to high-value products through solid-state fermentation by protease-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3》一文用蛋白酶增强的SCUT-3菌株实现了棉籽粕的高效降解利用,在增强了棉籽蛋白的消化利用率的同时,极其显著地降低了其中对动物有毒的棉酚含量。相关技术大幅提高了植物蛋白作为养殖动物饲料蛋白原料的性能,也有助于相关产品在人类营养(小肽营养)及植物营养(氨基酸肥)中的应用。
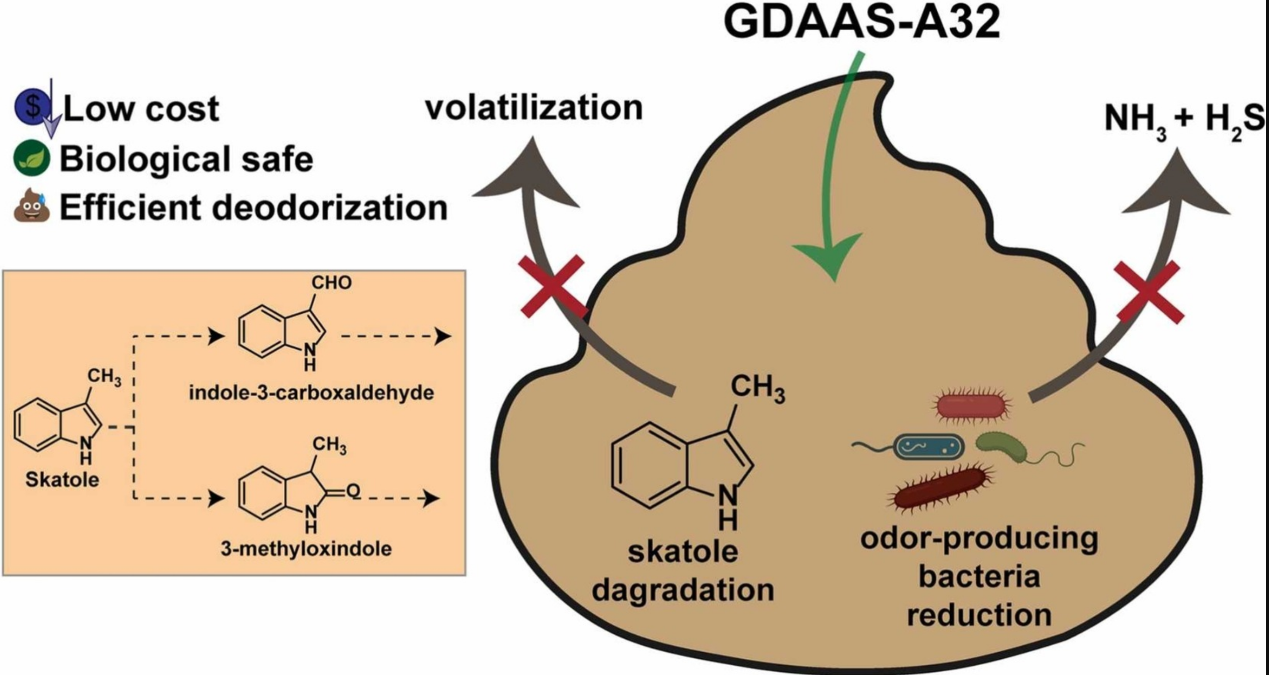
《Biodegradation of skatole by Bacillus subtilis GDAAS-A32 and its inhibition for odor emissions from swine manure》一文在细致解析枯草芽孢GDAAS-A32中类噬菌体的质粒中,存在粪臭素的氧化降解相关基因。将该菌泼洒在堆积猪粪中,可显著减少粪便中臭味分子的排放。相关菌株的进一步粪臭素降解改造,将有望用绿色的方法解决畜牧养殖业中粪便臭味的环境问题。
相关项目得到了广东省乡村振兴专项(2022-440000-4301030404-9580)和广州市科技攻关项目(202206010137)的支持。相关技术已经完成中试生产试验,正在建设万吨级生产线。项目的产业化实施将极大解决中国饲料蛋白原料豆粕鱼粉极度依赖进口的问题;产品在化妆品、保健品方向也有巨大的市场。
相关发表文章列表:
Deng J-J, Zhang J-R, Mao H-H, Zhang M-S, Lu Y-S, Luo X-C: Chitinases are important virulence factors in Vibrio for degrading the chitin-rich barrier of shrimp.International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2024:139215. (IF=8.5)https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.139215
Lu W-J, Zhang M-S, Lu D-L, Li Z-W, Yang Z-D, Wu L, Ni J-T, Chen W-D, Deng J-J, Luo X-C: Sustainable valorizing high-protein feather waste utilization through solid-state fermentation by keratinase-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3 using a novel promoter.Waste Management 2024, 174:528-538. (IF=7.1)https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2023.12.015
Cai H-H, Zhang M-S, Wu L, Li Z-W, Qin C, Liang C-Y, Deng J-J, Luo X-C: Identification of a Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3 aminopeptidase SsLap1 and its synergistic with endopeptidase Sep39 for peanut meal hydrolysis.Food Bioscience 2025:107216. (IF=5.9)https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2025.107216
Dai Z-J, Zhang M-S, Li Z-W, Lu D-L, Wu L, Qin C, Wang H-N, Deng J-J, Luo X-C: Highly efficient and sustainable bioconversion of cottonseed meal to high-value products through solid-state fermentation by protease-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3.Chemical Engineering Journal 2025:166481. (IF=13.2)https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.166481
Hu J-Y, Han X-Y, Chen H-P, Li J-Z, Wang Z-L, Luo X-C, Deng J-J: Biodegradation of skatole by Bacillus subtilis GDAAS-A32 and its inhibition for odor emissions from swine manure.Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2025, 13:115426. (IF=7.2)https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2025.115426
Lu D-L, Zhang M-S, Wang F-B, Dai Z-J, Li Z-W, Ni J-T, Feng W-J, Zhang F-G, Dai J, Wang H-N, et al: Nutritional value improvement of soybean meal through solid-state fermentation by proteases-enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3.International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2025:140035. (IF=8.5)https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140035
Ni J-T, Zhang M-S, Lu D-l, Lu W-j, Wu L, Yang Z-d, Qin C, Dai Z-j, Li Z-w, Feng W-j, et al: Bioconversion of agriculture by-products with functionally enhanced Streptomyces sp. SCUT-3: Fish skin as a model.Food Chemistry 2025, 463:141106. (IF=9.8)https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141106