Our research group focuses on developing bio-responsive polymeric systems for antimicrobial applications. To bridge the translation of antimicrobial peptides and responsive polymers into practical use, we design novel cationic oligomers and polymers, engineer self-assembled nano-vehicles, and formulate polymeric coatings with antimicrobial functionalities.
1. Redox-responsive cationic polymers and oligomers for antimicrobial application: We are dedicated to developing redox-responsive cationic polymers and oligomers to combat drug-resistant microorganisms. These agents deliver potent antimicrobial activity against drug-resistant microbes and biofilms; respond to ROS and glutathione to minimize toxicity to healthy tissues; avoid inducing drug resistance; and integrate antioxidant/anti-inflammatory effects for immune modulation. This design balances efficacy and biocompatibility, offering a robust solution for drug-resistant infections and biofilm-related challenges.
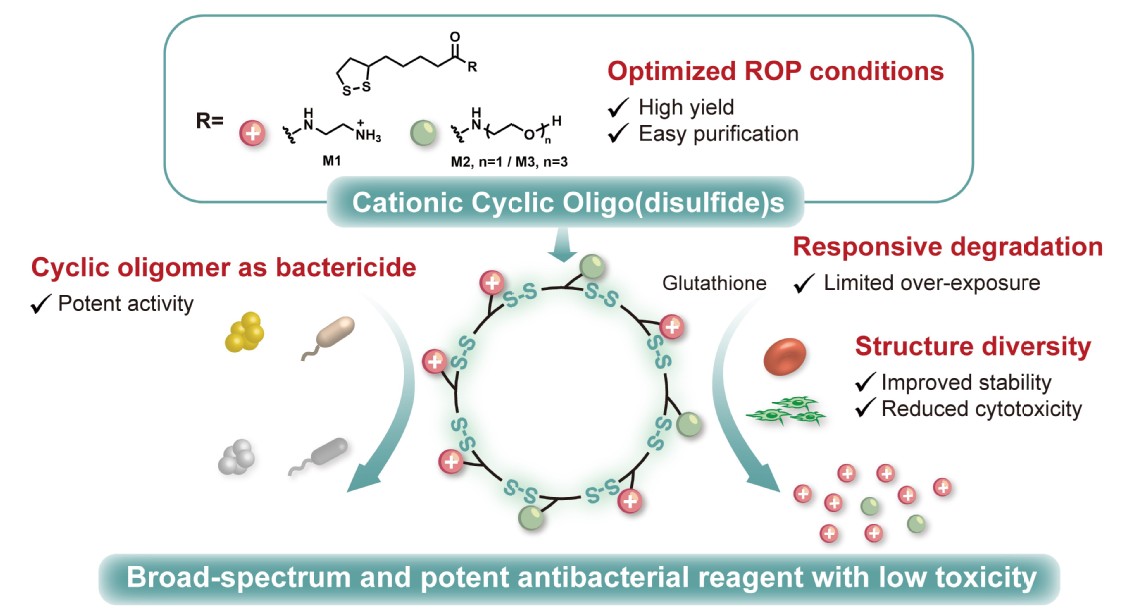
Representative publication: (1) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 6772-6785. (2) Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 6637-6649.
2. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS)-Peptide Amphiphiles as drug delivery vehicles: POSS-peptide amphiphiles nanocarriers address critical clinical challenges of hydrophobic peptide drugs, including poor water solubility, instability, and systemic toxicity. By conjugating hydrophilic POSS with functional peptides, this platform generates responsive nanocarriers with tunable self-assembly morphology. Leveraging synergistic dynamic bonding and peptide design, the customizable system enables high drug loading, controlled release, and combinatorial therapies for oncology and drug-resistant infections.
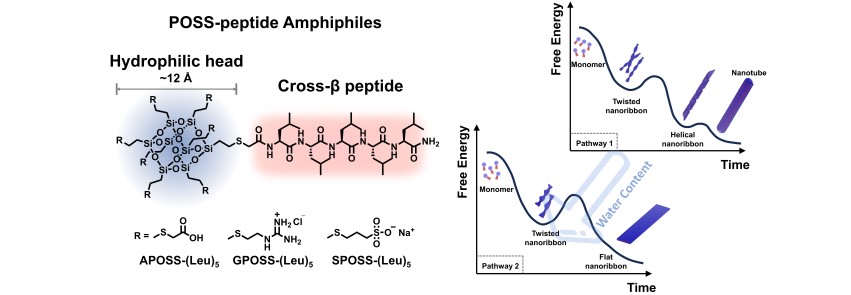
Representative publication: (1) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 64, e202420043. (2) Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 5071-5082.
3. Antibiotic-free antibacterial coatings: Antibiotic-free coatings combine natural antibacterial polysaccharides with antimicrobial nanoparticles, have been designed to achieve broad-spectrum bactericidal activity and local responsive drug release. This sustainable, multi-functional approach combats biofilms and nosocomial infections, offering a promising alternative to antibiotic-dependent strategies for healthcare surface disinfection.
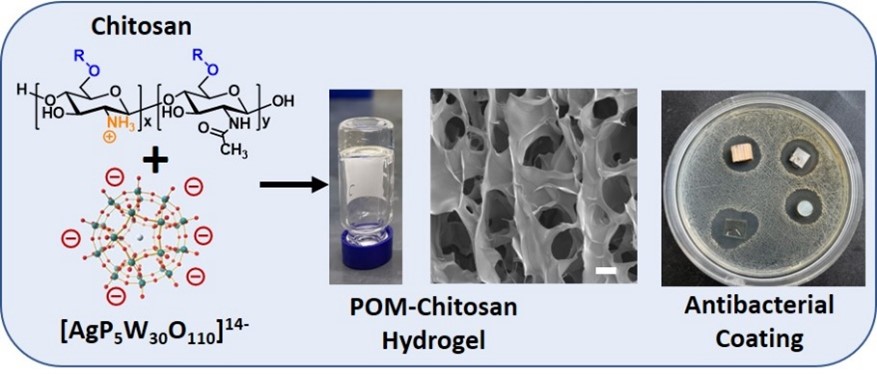
Representative publication: (1) Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 972-982.