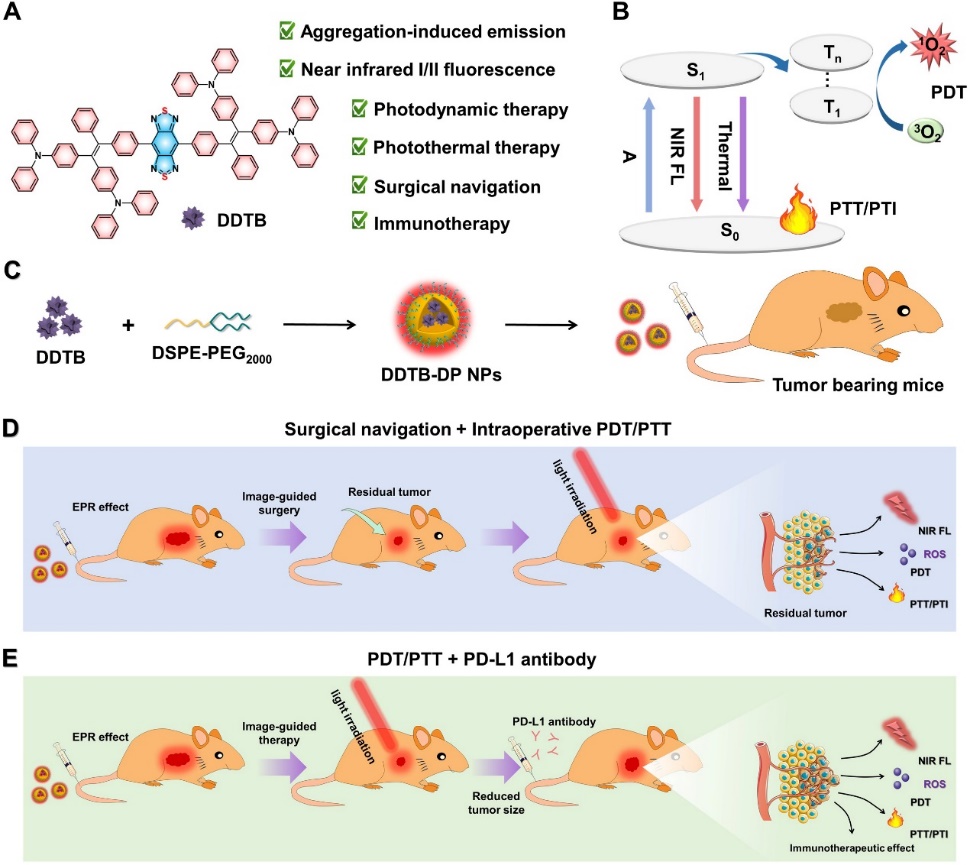
Multimodal therapy is attracting increasing attention to improve tumor treatment efficacy, but generally requires various complicated ingredients combined within one theranostic system to achieve multiple functions. Herein, we design a multifunctional theranostic nanoplatform based on a single aggregation-induced emission luminogen (AIEgen), DDTB, to integrate the near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence, photothermal, photodynamic and immunological effects. Intravenous injected AIEgen-based nanoparticles can efficiently accumulate in tumor with NIR fluorescence to provide preoperative diagnosis. Most of the tumors are excised under intraoperative fluorescence navigation, whereafter, some microscopic residual tumors are completely ablated by photodynamic and photothermal therapies for maximally killing the tumor cells and tissues. Up to 90% of the survival rate can be achieved by this synergistic image-guided surgery, photodynamic and photothermal therapies. Importantly, the nanoparticles mediated photothermal/photodynamic therapy plus programmed death-ligand 1 antibody significantly induced tumor elimination by enhancing the effect of immunotherapy. This theranostic strategy on the basis of a single AIEgen significantly improved the survival of cancer mice with maximized therapeutic outcomes, holds great promise for clinical cancer treatment.
Ph. D. candidate Ruming Jiang in our group is the first author of this article, and the related paper is available online at Advanced Materials (DOI: 10.1002/adma.202101158).
