| 祝贺苏晓竞同学在《ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces》上发表研究论文 |
| 发布时间: 2016-12-30 浏览次数: 939 |
|
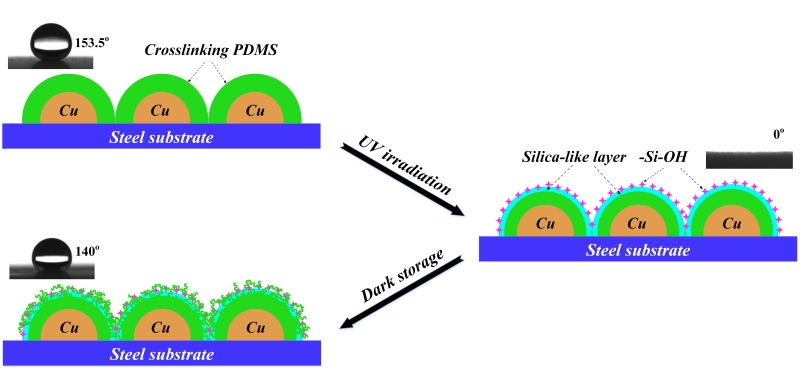
Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Superhydrophobic Surfaces on Steel Substrate: Fabrication, Reversibly Extreme Wettability and Oil-Water Separation Xiaojing Su, Hongqiang Li*, Xuejun Lai, Lin Zhang, Tao Liang, Yuchun Feng, and Xingrong Zeng* Abstract: Functional surfaces for reversibly switchable wettability and oil-water separation have attracted much interest with pushing forward an immense influence on fundamental research and industrial application in recent years. This article proposed a facile method to fabricate superhydrophobic surfaces on steel substrates via electroless replacement deposition of copper sulfate (CuSO4) and UV curing of vinyl terminated polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). PDMS-based superhydrophobic surfaces exhibited water contact angle (WCA) nearly to 160o and water sliding angle (WSA) lower than 5o, preserving outstanding chemical stability which maintained superhydrophobicity immersing in different aqueous solutions with pH values from 1 to 13 for 12 h. Interestingly, the superhydrophobic surface could dramatically switch to superhydrophilic state under UV irradiation, and then gradually recover to highly hydrophobic state with WCA at 140o after dark storage. The underlying mechanism was also investigated by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Additionally, the PDMS-based steel mesh possessed high separation efficiency and excellent reusability in oil-water separation. Our studies provide a simple, fast and economical fabrication method for wettability-transformable superhydrophobic surfaces and have the potential applications in microfluidics, biomedical field and oil spill clean-up.
论文链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b13901 |