1、超分子弹性体的基础研究 超分子弹性体是指以分子间非共价键构筑的、具有典型橡胶态交联弹性的一类弹性物质。因其三维交联网络并基于传统的共价键构建,超分子弹性体表现出诸多与传统弹性体(包括:硫化橡胶、热塑性弹性体等)不同的性质,是近年来国内外的一个研究热点之一。2008年,Leibler在Nature发表“Self-healing and thermoreversible rubber from supramolecular assembly”(Nature, 2008, 451(7181): 977-980)后,基于小分子间多重氢键的超分子弹性体的设计与合成在国内受到了极大的关注,本研究组的研究工作亦起步于此。 在超分子弹性体研究领域,本研究组主要关注以下方面的基础研究: (1)基于小分子间多重氢键作用的超分子弹性体的设计与合成; (2)超分子弹性体的三维交联网络的结构模型; (3)可自愈合的超分子弹性体的设计、合成及其自愈合机理。 目前主要的贡献包括: (1)以分子链极为柔顺的聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)主链替代Leibler所提出来的含多元环的碳链,合成得到了一类在常温和底纹下具有良好橡胶弹性,在常温可自愈合的超分子弹性体(SESi);进一步合成了基于单一的线形二元羧酸(端羧基低分子量聚硅氧烷)的超分子弹性体。
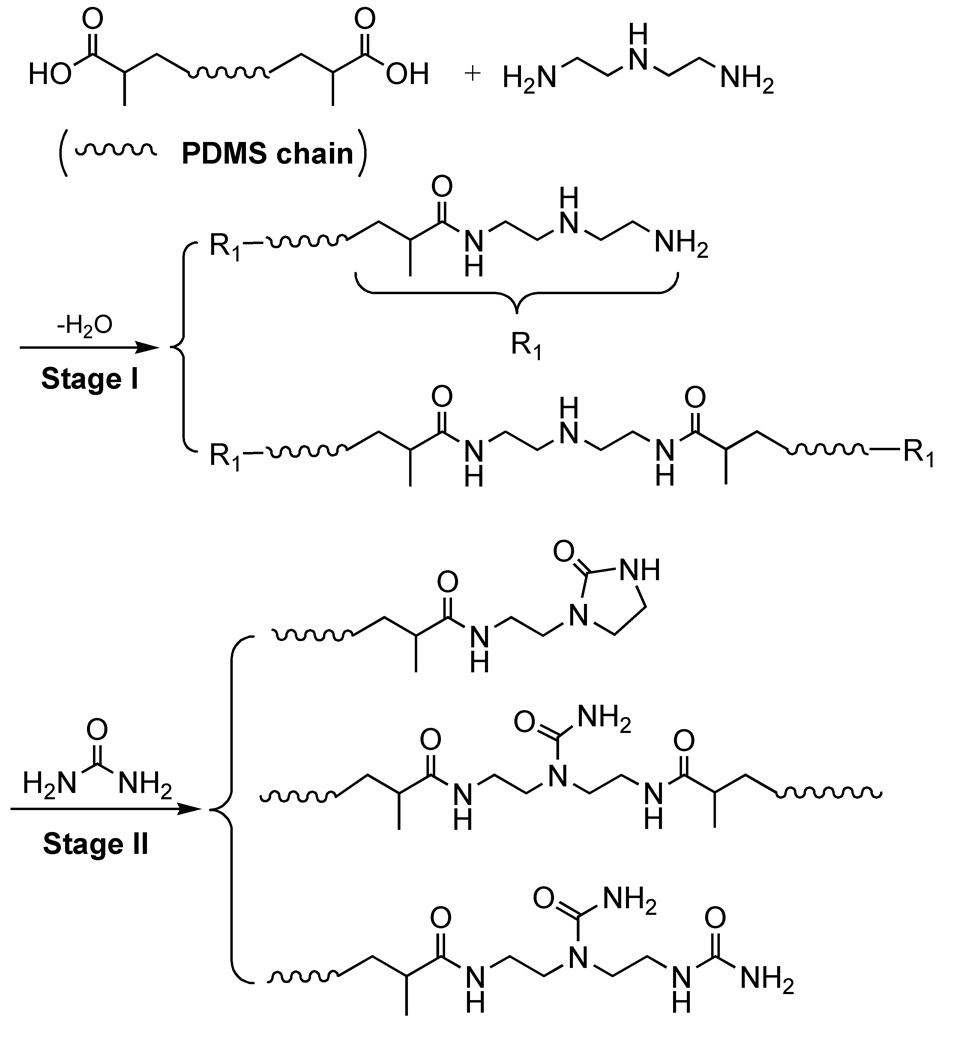
图1. SESi的合成路线 | 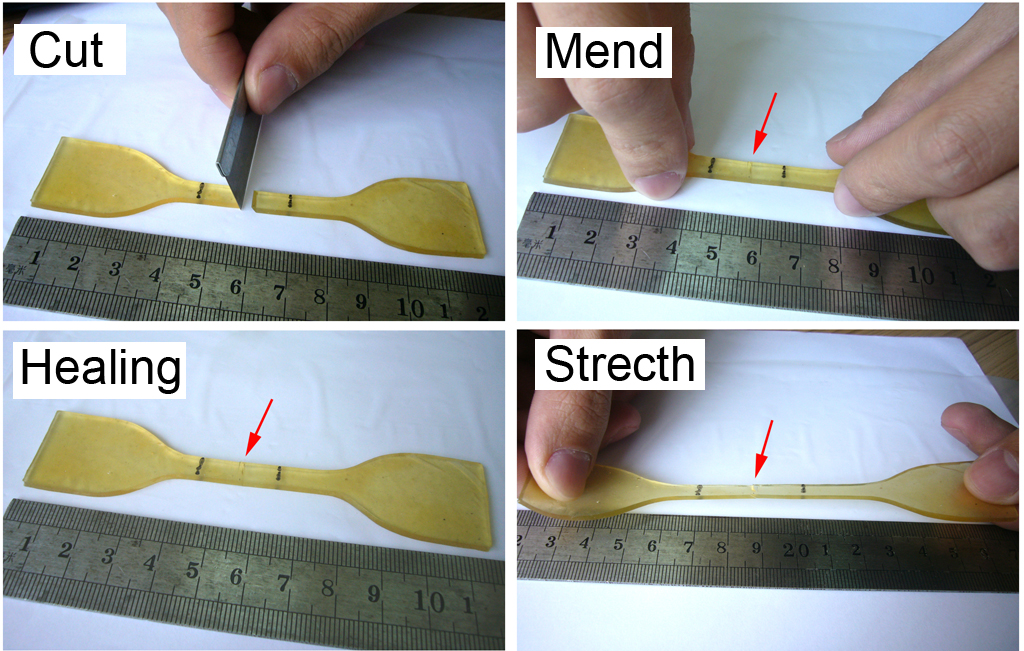
图2. SESi的自愈合示意图 |
(2)发现了一个以往被忽略的交联反应(1,1-二取代脲之间的缩合反应),指出Leibler所提出了完全基于氢键交联的超分子弹性体模型中存在不可控的共价交联;并在此基础上提出了一种基于可控共价/氢键杂化交联网络的新型超分子弹性体(HSE)。
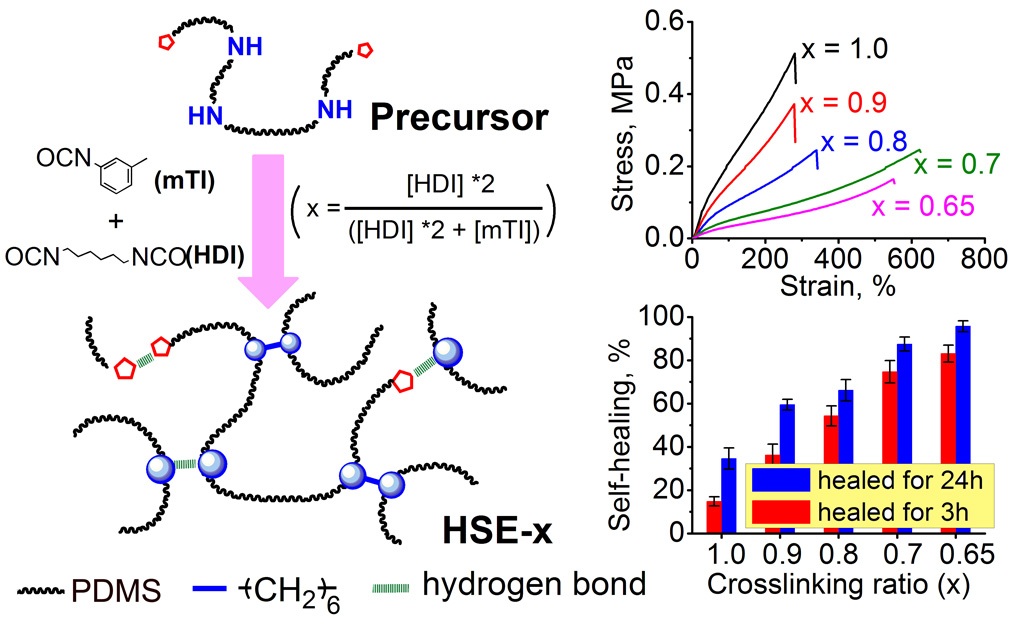
图3. HSE的合成路线及自愈合特性示意图 发表的相关论文:
[1] Yang You, Weiyan Huang, Anqiang Zhang*, Yaling Lin. A facile and controllable synthesis of dual-crosslinked elastomers based on linear bifunctional polydimethylsiloxane oligomers. Journal of Polymer Science, Part A Polymer Chemistry. 2016, 54, 3760–3768 [2] You Y, Zhang AQ, Lin YL. Crosslinking mechanism of supramolecular elastomers based on linear bifunctional polydimethylsiloxane oligomers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2016, 133(18): DOI: 10.1002/app.43385 [3] Yang L, Lin Y L*, Wang L S, Zhang A Q*. The synthesis and characterization of supramolecular elastomers based on linear carboxyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane oligomers. Polym. Chem., 2014, 5(1): 153-160 [4] Zhang A Q*, Yang L, Lin Y L*, Yan L S, Lu H C, Wang L S. Self-healing supramolecular elastomers based on the multi-hydrogen bonding of low-molecular polydimethylsiloxanes: Synthesis and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 129(5): 2435–2442 |
2、超分子弹性体的应用研究
聚硅氧烷超分子弹性体(SESi)因其具有良好的透明性和自粘性(与干燥皮肤粘结良好,与湿润的创口不粘结)、一定的吸水性和水汽透过率(透汽性),尤其适合作为皮肤创口敷料的基材。研究发现,SESi可为皮肤创伤提供洁净的湿性愈合微环境,有效地促进了伤口的愈合,其促进愈合的效果与已经商品化的3M公司的Tegaderm透明敷料类似。 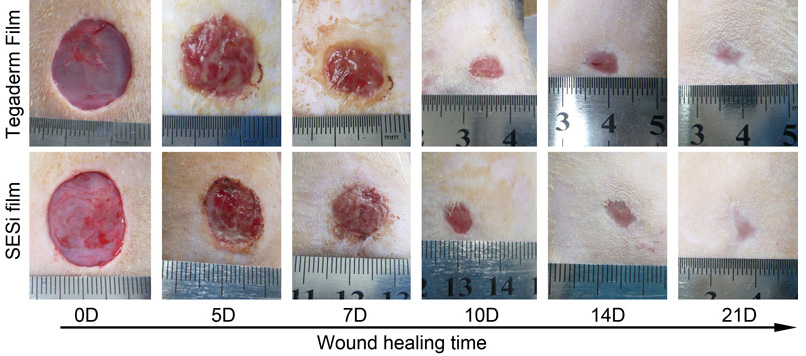
(A)大体观察 | 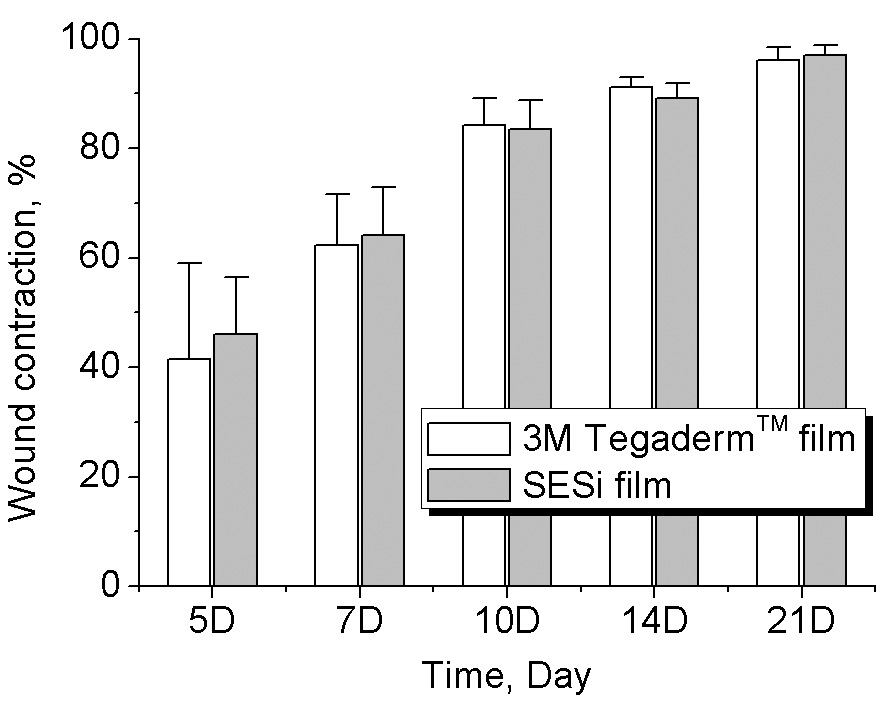
(B)愈合率比较 |
图4. SESi薄膜敷料和Tegaderm透明敷料对大鼠全层皮肤切除创口的促进愈合作用示意图:(A)大体观察,(B)愈合率比较 发表的相关论文: [1] Deng Wenwen, Lei Yufeng, Zhou Shengwen, Zhang Anqiang, Lin Yaling. Absorptive supramolecular elastomer wound dressing based on polydimethylsiloxane–(polyethylene glycol)– polydimethylsiloxane copolymer: preparation and characterization. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(57): 51694-51702. [2] Zhang A Q*, Deng W W, Lin Y L, Ye J H, Dong Y M, Lei Y F, Chen H T. Novel supramolecular elastomer films based on linear carboxyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane oligomers: preparation, characterization, biocompatibility, and application in wound dressings. J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed., 2014, 25(13): 1346-1361 [3] Zhang A Q*, Yang L, Lin Y L*, Lu H C, Qiu Y H, Su Y L. Supramolecular elastomer based on polydimethylsiloxanes (SESi) film: synthesis, characterization, biocompatibility, and its application in the context of wound dressing, J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed., 2013. 24(16): 1883 - 1899 |
|





