Gelation of metal oxide clusters for redox-active proton conductors in supercapacitor
Xinpei Li, Linkun Cai, Mu Li, Mingxin Zhang, Qianjie Zhou, Kun Chen, Panchao Yin*
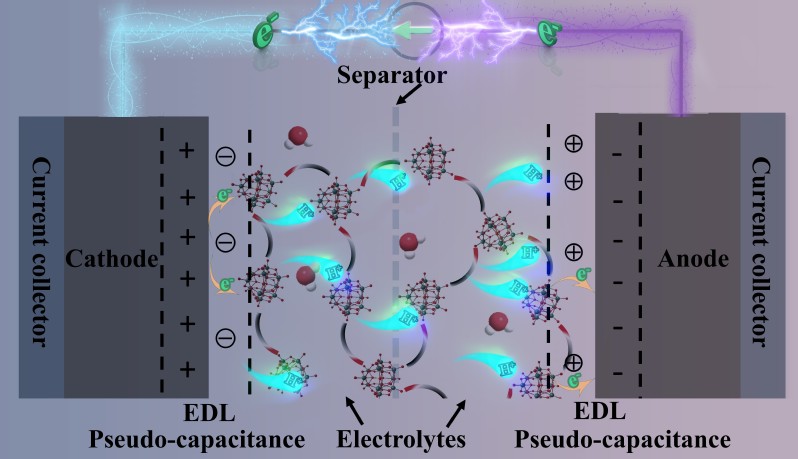
The redox-active electrolytes can cost-effectively enhance the energy densities of energy storage devices, which, however, face the challenge of short cycle-life and poor compatibility to device electrodes. Here, redox-active hydrogels can be facilely prepared with promising proton conductivities and electrode compatibility from the supramolecular complexation of neomycin sulfate and metal oxide clusters. Metal oxide clusters serve as both proton and electron reservoirs to simultaneously improve the proton conductivities of electrolytes and super redox properties for the pseudo-capacitance, leading to the enhancement of the energy densities of supercapacitors. Proton conduction follows typical Grotthuss mechanism through the fast dynamic arrangement of hydrogen bonding networks among water, neomycins and metal oxide clusters. With activated carbon as electrodes, the assembled supercapacitors of the hydrogels show excellent cycle stabilities. The supramolecular complexation of reversible redox active cluster opens an avenue for facile assemblies of highly efficient and robust super-capacitors.
文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013468622000160

