Polymerization-Induced Microphase Separation of Polymer-Polyoxometalates Nanocomposites for Anhydrous Solid State Electrolytes
Lu Liu , Zicheng Wu , Zhao Zheng , Qianjie Zhou , Kun Chen , Panchao Yin
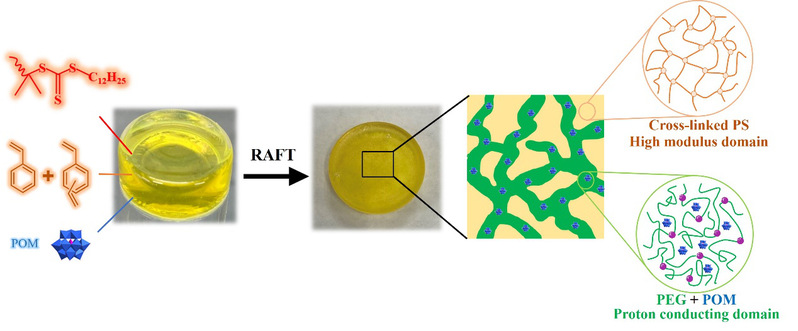
we present a facile, scalable, one-step synthetic protocol to fabricate high-temperature anhydrous conductive nanocomposites based on POMs and PEG5k-b-P(S-co-DVB) via polymerization-induced microphase separation. The POMs-PEG5k-b-P(S-co-DVB) nanocomposites exhibit a bi-continuous morphology, in which the POMs are uniformly dispersed in the PEG block (PEG/POM) to form a conducting pathway that successfully realizes the effective transportation of protons and lithium ions. The highly cross-linked PS domains (P(S-co-DVB)) serve as mechanical support and provide outstanding mechanical properties and thermal stability. The prepared nanocomposites overcome the safety and stability issues of conventional SSEs when working under high temperature conditions, and avoid the drawback that small molecules of acids in existing SSEs tend to leach out from the polymer matrix. Due to the broad availability of POMs and polymers with different functionalities, the SSE system can be facilely extended to a variety of functional electrolytes, e.g. sodium-ion conductive electrolytes, which can extend the design of multifunctional SSE materials.
我们报告了一种基于聚合诱导微相分离 (PIMS) 的简便通用的一锅合成法,以生成具有双连续相微相分离的聚合物纳米复合材(PNC)。在该PNC中,POM均匀地分散在PEG域中 (PEG/POM),以形成实现质子和锂离子有效转移的导电路径,而作为机械支撑的高度交联聚苯乙烯域 (P(S-co-DVB)) 提供优异的机械性能和热稳定性。所制备的纳米复合材料克服了传统SSE在高温条件下工作时的安全性和稳定性问题,并且避免了现有SSE中的小分子酸容易从聚合物基体中渗出的缺点。这项研究拓宽了燃料电池和锂离子电池在极端环境中的应用。同时,由于具有不同功能的POM和聚合物的广泛可调性,该系统可以轻松地扩展到多种功能性电解质,例如钠离子导电电解质,扩展了多功能SSE材料的设计。

