Zhao Zheng, Qianjie Zhou, Mu Li, Panchao Yin*
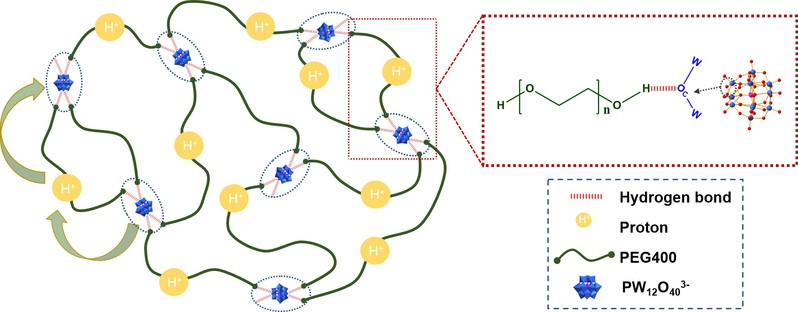
Sub-nm-scale metal oxide clusters (PW12O403−) show high solubility in the melt of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and the obtained semi-solid nanocomposites show promising proton conductivities under ambient conditions. Suggested from scattering studies, the clusters are homogeneously dispersed in the PEG melt at the molecular scale with high loading amounts (70 wt%) and the formed real solutions can be stable for months with no aggregation or phase separation. The conductivities of the nanocomposites which are governed by the concentrations of PW12O403− can reach as high as 1.01 × 10−2 S cm−1at the highest concentration. Due to the dynamic cross-linking hydrogen bonding between clusters and PEG, the nanocomposites behave like solids with negligible flow at high concentrations of clusters. Upon the application of high-speed shear forces (>32 s−1), the composites can flow with continuously decreasing viscosities. The shear thinning properties of the nanocomposites enable their convenient processing into required morphologies and the wettability of electrolytes to electrodes under typical high shear rate processing conditions and the safety of the produced devices can be ensured by their solid-like properties in the static state.
多金属氧酸盐(POMs)是一大类主要由金属-氧多面体连接构成的结构明确、大小在纳米级别的分子簇。作为小分子与纳米粒子之间的过渡区,亚纳米分子簇(主要为Lindqvist和Keggin型)具有较高的比表面积、催化效率、质子导电性以及良好的稳定性。为提高多酸稳定性,日本东京大学Sayaka Uchida课题组,将聚乙二醇(PEG)放入多酸晶体的孔道中。所形成的晶体复合物,在443 K的非湿环境中,可实现1.2 x 10-5 S cm-1的电导率(J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 234, 9)。同时,殷盼超教授课题组利用中子散射技术证明,在此聚乙二醇-多酸晶体复合材料中,PEG链正好充当了质子传递的桥梁,质子与PEG的O原子结合,随着聚合物链的纵向移动实现质子的有效传递(J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 19, 5772-5777)。但在此体系中,PEG链被限制在POM晶体孔道中,这实际上极大的限制了聚合物链的运动,材料电导率不高,且此质子导体材料未保留其有机组分的优点,力学性能较差。针对以上问题,此工作通过降低多酸的结晶能及其对聚合物链的限制作用,在提高聚乙二醇-多酸复合材料电导率的同时,保证其拥有良好的力学性能和可加工性。
Keywords: Polyoxometalates Polyethylene glycol Pronton conductor material
文章链接:https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2019/sc/c9sc02779c

