Jie Hu, Mu Li, Kun Chen,* and Panchao Yin*
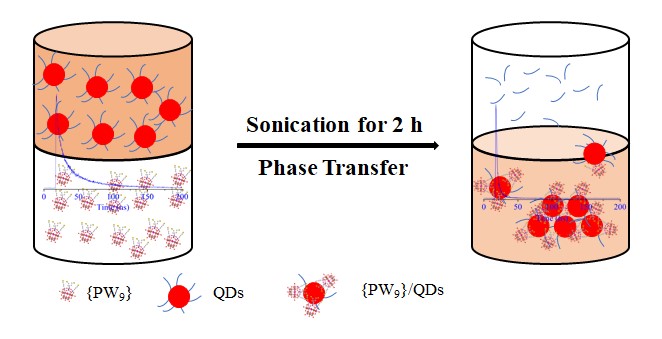
A co-assembly protocol of quantum dots (QDs)-polyoxometalates (POMs) hybrids is developed using Keggin-type POMs as surface capping ligands. Phase transfer strategy is used to prepare POM-QDs nanocomposites. These newly developed hybrid materials have been explored for their optical properties and aggregation behavior in solutions. UV/Vis and FT-IR are used to reveal the optical properties of POM-QDs. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) are applied to characterize the co-assembled core-shell structures of POM-QDs complexes under different reaction conditions. A general trend to be noted is that the average photoluminescence (PL) lifetime of QDs decreases after phase transfer. The lifetime attenuation is caused by the surface property change of newly obtained POM-QDs complexes, which is resulted from the changed band edge recombination and shallow trap assisted recombination.
我们采用一种共组装策略,将修饰后的Keggin型多金属氧酸盐作为表面配体,通过“爪子”嫁接到量子点上。相转移方法被用来制备POM-QDs 纳米材料。探究了制备的新纳米材料的光学性质和溶液中聚集行为。紫外和红外被用来研究新纳米材料的光学性质,X-射线小角和透射电镜表征了不同条件下的形貌,证明了形成了壳核结构。新纳米材料总的趋势是平均光致发光(PL)寿命在相转移后降低。荧光寿命降低是因为新获得的POM-QDs配合物的表面性质发生了变化,引起带边沿重组和浅陷阱辅助复合。
Keywords:Quantum dots Polyoxometalates Phase Transfer Optical properties nanocomposites
文章链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ejic.201900498

