A General Approach to Access Morphologies of Polyoxometalates in Solution by Using SAXS: An Ab Initio Modeling Protocol†
Mu Li, Dr. Weiyu Wang , Prof. Dr. Panchao Yin*[a]
[a] South China Advanced Institute for Soft Matter Science and Technology and State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640 (P.R. China)
[†] SAXS=small-angle X-ray scattering
Chem.-Eur. J. 2018, 24 (25), 6639-6644
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201800344
Publication Date (Web): February 23, 2018
Copyright © 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
*E-mail: yinpc@scut.edu.cn
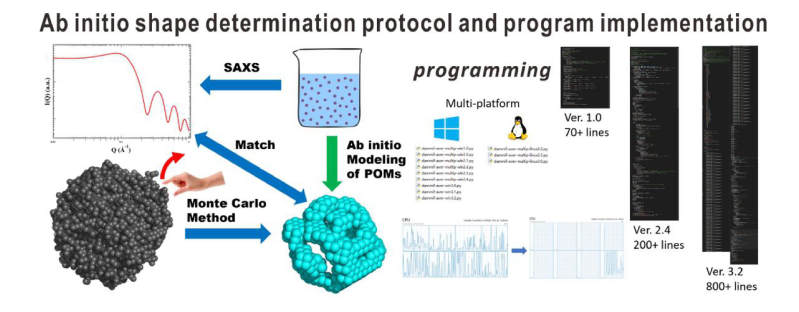
Herein, we reported a general protocol for an ab initio modeling approach to deduce structure information of polyoxometalates (POMs) in solutions from scattering data collected by the small‐angle X‐ray scattering (SAXS) technique. To validate the protocol, the morphologies of a serious of known POMs in either aqueous or organic solvents were analyzed. The obtained particle morphologies were compared and confirmed with previous reported crystal structures. To extend the feasibility of the protocol to an unknown system of aqueous solutions of Na2MoO4 with the pH ranging from −1 to 8.35, the formation of {Mo36} clusters was probed, identified, and confirmed by SAXS. The approach was further optimized with a multi‐processing capability to achieve fast analysis of experimental data, thereby, facilitating in situ studies of formations of POMs in solutions. The advantage of this approach is to generate intuitive 3D models of POMs in solutions without confining information such as symmetries and possible sizes.

