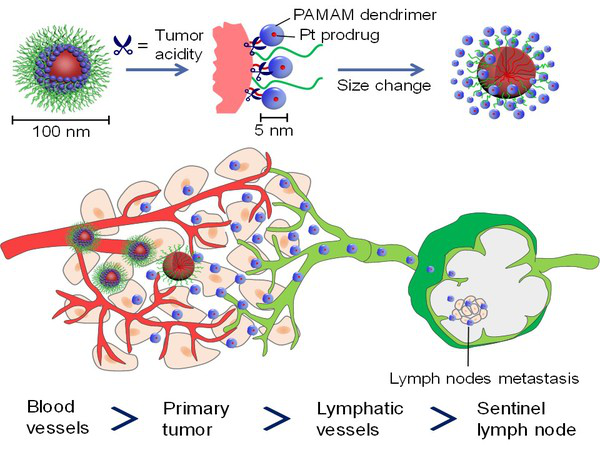
Tumor metastasis is the primary cause of death for cancer patients. How to effectively inhibit tumor metastasis is a difficult problem for cancer treatment. Lymph nodes are the primary site of metastasis of epithelial-derived tumors such as breast cancer. Clinical studies have shown that patients with lymph node metastasis have a poor prognosis. Therefore, it is of great scientific and clinical significance to develop effective methods to intervene lymph node metastasis. Removal of lymph node metastases with conventional surgery and radiation can cause lymphedema, pain, infection, and other side effects. Development can improve the efficiency of drug delivery in lymph nodes, and increasing drug concentration in lymph nodes is an effective means.
To address this problem, researchers from the nanomaterials and biomaterials team in the South China University of Technology have proposed a new strategy to improve the delivery of tracers or drugs through tumor lymphatics to lymph nodes. Their previous development of tumor size of the acidity response shift iCluster delivery system can enhance the characteristics of tumor infiltration. The researchers in this study further find that iCluster in tumor tissues, a small size particles can be more effective to enter primary tumor lymphatic vessels, and enter into the lymph nodes, can kill existing tumor cells. Quantitative analysis and fluorescence imaging experiments clearly prove that iCluster is beneficial to the enrichment of fluorescent tracers and anti-tumor drugs in sentinel lymph nodes in the presence of primary tumor. The researchers further confirm in breast cancer models with early and late metastasis that iCluster can inhibit the occurrence of metastasis, prolong the survival period of mice and effectively improve the efficacy of anti-tumor metastasis. Research results Enhanced Primary Tumor Penetration Facilitates Nano-particle Draining into Lymph Nodes after Systemic Injection for Tumor Metastasis Inhibition is published in the international authoritative academic journal ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 8648-8658, the full text links to https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.9b03472.
The first author of the paper is Dr. Liu Jing, and the corresponding author are Dr. Li Hongjun and researcher Du Jinzhi. South China University of Technology is the first author and corresponding unit of the paper. The research is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Science and Technology foundation, the Guangdong Outstanding Youth Fund, and the Innovation Team of the Pearl River Talent Program of Guangdong province. After the publication of The research results, ACS News Service Weekly PressPac carries out a special report entitled Nanoparticle therapy targets node metastases, and it is reprinted by Science Daily, Phys.org, the Medical News, Nanowerk, Technology Networks and other media.

