Major code: 081001 Duration: 4 years
Cultivation Goals:
Oriented to the national One Belt, OneRoad strategy and the Dual carbon goal, this major relies onthe emerging development and urban renewal needs of the Guangdong-HongKong-Macao Greater Bay Area urban agglomeration, cultivating both family andcountry feelings and global vision, solid engineeringfoundation, and mastery of emerging cutting-edge technologies, Threeforces (learning, thinking, action) excellent, all-round development ofthe Three innovation (innovation, creation, entrepreneurship)talents. Specifically, it includes the following three objectives:
(1) Cultivation Goal 1: Practice the core values ofsocialism, uphold the spirit of craftsmen, have a sound personality and noblehumanistic feelings, resilience and confidence to overcome difficulties, alifelong learning mentality, and obtain a strong sense of professional honorand pride;
(2) Cultivation Goal 2: Master the basic concepts,knowledge system and common tools of civil engineering, understand the newneeds and new formats of industries and disciplines, and have a certaininterdisciplinary knowledge reserve, especially digital and informationtechnology in the future development of low-carbon construction and resilientcities;
(3)Cultivation Goal 3: Have the comprehensive abilityto think independently, find problems, analyze problems, and solve complexcivil engineering problems, and have good self-management skills, communicationand teamwork skills, leadership, and the ability to adapt tointernationalization and cross-cultural communication.
Through four years of study, graduates can beengaged in survey, design, construction, project management, education,scientific research and other work in the field of infrastructure such asconstruction, bridges, highways, tunnels and new infrastructure, and reach thesame level as the professional qualification of civil engineers in about fiveyears after graduation, become the technical backbone or senior managementpersonnel in civil engineering and related fields, or obtain a master's degreeor above from a first-class university.
Graduation Requirements:
№1.Moralcultivation: Moral cultivation understands and masters the worldview andmethodology of learning, has good ideological character and social morality,has a sense of family and country and social responsibility, and can practicethe core values of socialism.
No1.1 Understand and master the scientific world view andmethodology, and have good ideological character and social morality
No1.2 Have a sense of family and country and socialresponsibility, and be able to practice the core values of socialism.
№2.EngineeringKnowledge: Ability to apply mathematics, natural sciences, engineeringfundamentals, and expertise to solve complex engineering problems in the fieldof civil engineering.
No2.1 Be able to apply mathematics, natural sciences,engineering foundations and professional knowledge to establish correctmathematical and mechanical models and express complex engineering problems incivil engineering.
No2.2 Be able to apply engineering foundation andprofessional knowledge to deduce and solve the correctness of the model.
No2.3 Be able to apply engineering foundation andprofessional knowledge to propose several solutions to complex engineeringproblems in civil engineering, and analyze, compare and optimize.
№3.ProblemAnalysis: Able to apply the basic principles of mathematics, natural sciencesand engineering sciences to identify, express, and analyze complex engineeringproblems in civil engineering through literature research to obtain effectiveconclusions.
No3.1 Be able to apply the basic principles ofmathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences to identify and judgethe key links in complex engineering problems in civil engineering.
No3.2 Be able to apply the basic principles ofmathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences, and use drawings andwords to effectively express complex engineering problems in civil engineering.
No3.3 Be able to apply the basic principles ofmathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences, and use domestic andforeign literature, norms, standards, etc. to systematically analyze complexengineering problems in civil engineering, and seek alternative solutions toobtain effective conclusions.
№4.Design/DevelopSolutions: Design creative solutions to complex engineering problems and designsystems, components, or processes to meet identified needs, with dueconsideration for public health and safety, costs throughout the life cycle,net-zero carbon, and resource, cultural, social, and environmental factors.
No4.1 Be able to design (develop) systems, structures,components (nodes) and construction plans that meet the specific needs of civilengineering.
No4.2 can consider the influence of social, health,safety, legal, cultural and environmental factors in engineering design andconstruction plans according to the specific needs of civil engineering.
No4.3 Be able to optimize engineering design andconstruction schemes, and have a sense of overall and innovation when proposingsolutions to complex engineering problems.
№5.Research: Beable to conduct research on complex engineering problems in civil engineeringbased on scientific principles and using scientific methods, includingdesigning experiments, analyzing and interpreting data, synthesizinginformation, etc., to obtain reasonable and effective conclusions, and applythem to engineering practice.
No5.1 Use the basic principles and operational skills ofcivil engineering related experiments, have the ability to scientificallydesign and implement experiments for complex engineering problems in civilengineering, and correctly collect experimental data and information, and haveexperimental safety awareness.
No5.2 Be able to analyze and interpret experimentalresults based on scientific principles and scientific methods, obtainreasonable and effective conclusions through information synthesis and applythem to engineering practice, and investigate and analyze solutions to complexprocess problems through literature research or related methods.
№6.Use of tools:Ability to select, use and develop appropriate technologies, resources, modernengineering tools (equipment) and information technology to solve complexengineering problems, including simulation, analysis and prediction of complexengineering problems, and to understand their limitations.
No6.1 Grasp the technologies, resources, modernengineering tools and information technology tools commonly used in the fieldof civil engineering and understand their limitations.
No6.2 Be able to reasonably select, use or developappropriate technologies, resources, modern engineering tools and informationtechnology tools for analysis, calculation and design for complex engineeringproblems.
No6.3 Ability to correctly simulate and predict complexengineering problems using modern engineering tools and information technologytools, and be able to understand their limitations and reasonably evaluate thevalidity of analysis results.
№7.Engineers and the World:Aware of and understanding the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal(SDG17) and able to analyse and evaluate the design, construction and operationof civil engineering projects and solutions to complex engineering problems,including social, economic, sustainability, health, legal and environmentalimpacts, based on relevant background knowledge and standards of civilengineering. and understand the responsibilities expected of a civil engineer.
No7.1 Be able to reasonably analyze and evaluate thedesign, construction and operation of civil engineering projects and solutionsto complex engineering problems based on civil engineering laws, regulationsand technical standards.
No7.2 Be able to understand and evaluate the social,health, safety, legal, cultural, environmental, and sustainable developmentimpacts of engineering practices on complex engineering problems in civilengineering, as well as understand the constraints of the environment onengineering.
No7.3 Understand new materials, new processes and newmethods of civil engineering, pay attention to energy conservation and emissionreduction, and pay attention to the use of energy conservation andenvironmental protection technical solutions; Understand the new requirementsof social development for civil engineers.
№8.Ethics: Applyethical principles and devote ourselves to the practice and norms ofprofessional ethical engineering; and comply with relevant national andinternational laws. Demonstrate an understanding of the need for diversity andinclusion.
No8.1 Possess the necessary knowledge and literacy ofhumanities and social sciences, correct values and a sense of socialresponsibility, and a healthy body and a sound personality.
No8.2 Be able to understand and abide by the professionalethics and norms of the project in the practice of civil engineering projects,have legal awareness, and be responsible, contribute to the country and servethe society.
No8.3 Understand the responsibilities of civil engineersin relation to public health, public safety, society and culture, and the law.
№9.Individualand collaborative team work: Ability to take on the roles of individual, teammember, and leader in a diverse and inclusive team when solving complexengineering problems in the civil engineering profession.
No9.1 Ability to actively cooperate and cooperate withothers in a multidisciplinary environment, and be able to independentlycomplete tasks assigned by a team.
No9.2 Ability to take on the role of team member orleader in a multidisciplinary context, with organizational and coordinationskills.
№10.Communication:Ability to effectively communicate and communicate with industry peers and thepublic on complex engineering issues in the civil engineering profession,including writing reports and design manuscripts, making statements, andarticulating or responding to instructions; Have an international perspectiveand be able to communicate and exchange in a cross-cultural context.
No10.1 Have good writing and language skills, and be ableto effectively communicate and exchange with industry peers and the public oncomplex engineering issues in civil engineering through written and oral means.
No10.2 Have a certain international vision, understandthe international development trend of civil engineering related industries,have the language and written communication skills of cross-culturalcommunication, and be able to effectively communicate and exchange onprofessional issues in a cross-cultural context.
№11.ProjectManagement and Finance: Apply knowledge and understanding of engineeringmanagement principles and economic decision-making in relation to the civilengineering profession and apply it to your own work as a member and leader ofa team managing projects and multidisciplinary environments.
No11.1 Understand and master the principles ofengineering management and economic decision-making methods, and understand theengineering management and economic decision-making issues in the full-cycledesign of engineering projects.
No11.2 Ability to apply engineering management principlesand economic decision-making methods in the design and development of solutionsin a multidisciplinary environment to make sound leadership, organization andmanagement decisions in civil engineering projects.
№12.Continuouslifelong learning: the ability to learn independently and for lifelong learningaccording to the needs of personal and professional development, with theawareness of self-directed learning and lifelong learning, and the ability toadapt to new developments in civil engineering.
No12.1 Aiming at personal and professional developmentneeds, have the ability to learn independently, and have a sense of lifelonglearning.
No12.2 Ability to understand and track trends in civilengineering disciplines, and have the ability to adapt to emerging technologiesand think critically.
Matrix of the relationship between training objectives and graduationrequirements:
Cultivation Goals Graduation Requirements: | Cultivation Goal 1 | Cultivation Goal 2 | Goal 3 |
Graduation Requirement 1 | ● | ● | ● |
Graduation Requirement 2 |
| ● | ● |
Graduation Requirement 3 |
| ● | ● |
Graduation Requirement 4 |
| ● | ● |
Graduation Requirement 5 | ● | ● | ● |
Graduation Requirement 6 |
| ● | ● |
Graduation Requirement 7 | ● |
| ● |
Graduation Requirement 8 | ● |
| ● |
Graduation Requirement: 9 | ● |
| ● |
Graduation requirement 10 | ● |
| ● |
Graduation Requirement 11 |
| ● | ● |
Graduation Requirement 12 | ● |
| ● |
Major Introduction:
The Department of Civil Engineering, where the civilengineering major is located, is one of the six departments at the beginning ofthe establishment of South China University of Technology (formerly South ChinaInstitute of Technology), and its history can be traced back to the Departmentof Architectural Engineering of Guangdong Xiangqin University of Engineering in1933. Facing the major needs of national civil engineering and infrastructureconstruction, this major has successively trained more than 10,000 seniortechnical talents in engineering design, construction and management in thedirection of building structure, underground structure, road and bridgeengineering for the country, and has an important influence and good reputationin China's mainland, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan regions and Southeast Asiancountries. In 2003, the civil engineering major was rated as a famous brandmajor in Guangdong Province. In 2010, it became a characteristic major inGuangdong Province and was listed as the first batch of OutstandingEngineer Education and Training Program implementation majors of theMinistry of Education. In 2018, it passed the national evaluation(certification) of civil engineering majors in colleges and universities forthe fifth time. And in 2019, it became the first batch of national first-classprofessional construction sites.
The civil engineering discipline supported by thismajor is the first discipline in South China to have a first-level disciplinedoctoral program and a postdoctoral research station, and has formed a completebachelor's-master's- The doctoral talent training system has high-leveldiscipline platforms such as the National Key Laboratory of SubtropicalArchitecture and Urban Science and the Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory ofModern Civil Engineering Technology, which fully guarantees the effective developmentof experimental teaching and scientific research. There are nearly 70 full-timeteachers in this major, as well as a number of honorary professors, part-timeprofessors and consulting professors, forming a stable teaching team withreasonable knowledge, professional titles and age structure. At present, themajor has established 3 on-campus college students' innovation ability trainingbases and more than 40 off-campus industry-university-research practiceteaching and practice bases. It has established short-term exchange programswith many well-known universities at home and abroad, and signed multi-leveljoint training programs with many famous universities in North America, Europe,Australia and other countries such as undergraduate, master's and doctoraldegrees.
This major follows the trainingconcept of solid foundation, wide caliber, and specializedfrontier, relies on high-level discipline platforms such as the NationalKey Laboratory of Subtropical Architecture and Urban Science, and the unique industrialadvantages of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, combined withworld-class super-large engineering projects, to provide students withproduction, teaching, research, learning, innovation, andcompetition An integrated and diverse training environment.
Major Features:
1. Based on the seriesof mechanics theories and engineering structure theories, the curriculum systemdesign is interdisciplinary and empowered by artificial intelligence generaltechnology to improve students' civil, mechanical, computer and automation andother professional adaptability;
2. Relying on theuniversity's high-level discipline platform and the Greater Bay Area JointInternship Base, it integrates classroom teaching and large-scale projectpractice to cultivate students' ability to solve complex engineering problems.
3. Aiming at thefrontier of disciplines and industries, we carry out modular whole-processcustomized training to enhance students' long-term competitiveness and industryleadership ability.
DegreeAwarded: Bachelor ofEngineering
CoreCourses (10):
Theoretical Mechanics III.,Mechanics of Materials, Engineering Surveying and Mapping and DigitalArchitecture, Structural Mechanics, Fluid Mechanics, Engineering Geology andEngineering Materials, Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Theory of ConcreteStructures, Theory of Steel Structures, Principles of Engineering Constructionand Cost Management
FeaturedCourses:
Freshman Seminar (6courses):
Intelligent Transportation andSustainable Development, Digital Design and Intelligent Construction,Engineering Management in the Era of Artificial Intelligence, Digital TwinWatershed and Future Water Conservancy, Future Urban Science: Intelligent Designand Sustainable Systems, New Materials, New Structures, and New Engineering:Application of Mechanical Thinking
Frontier Courses (30courses):
6 cutting-edgemodules with 5 courses each.
Module 1:High-performance building structure and low-carbon construction (green buildingmaterials and low-carbon construction, green and intelligent design of humansettlements, high-performance materials and engineering applications,prefabricated modular construction and engineering applications, intelligentoptimization design of high-rise building structures).
Module 2:Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of the Whole Life Cycle of EngineeringStructures (Wind and Vibration Effect and Control of Mega Structures,Monitoring Technology of Construction Process of Large and Complex Structures,Analysis and Emergency Response of Engineering Safety Accidents, EarthquakeDisaster Prevention and Mitigation of Engineering Structures, Fire Effect andPrevention of Building Structures).
Module 3:Intelligent Construction and Digital Operation and Maintenance of EngineeringStructures (Frontier and Practice of New Complex Structure ConstructionTechnology, Structural Health Monitoring Internet of Things and Data Science,Structural Intelligent Perception and Engineering Diagnosis, High-performanceStructure Optimization and Algorithm Design, Urban Digital Operation andManagement).
Module 4:Urban Marine Geotechnical Engineering and Underground Space Development(Environmental Geotechnical Engineering, Smart Underground Space andEngineering, Coastal Soft Foundation Treatment and Underground Space ExcavationSupport, Intelligent Diagnosis and Repair of Service Performance of UndergroundStructures, Intelligent Rock Mass Analysis and Green Underground StructureDesign).
Module 5: Newtechnologies for major transportation infrastructure construction (digitalbridge engineering and AI design, digital construction technology for tunnelengineering, bridge structure evolution - innovative exploration of steel andconcrete combination, bridge intelligent detection technology and machinevision application, new generation bridge and tunnel maintenance technology)
Module 6:Green and resilient road construction and maintenance integration technology(road survey and design, green and resilient road construction and maintenancetechnology, future road structure and materials, modern transportationinfrastructure simulation technology, roadbed and slope design and safety).
School-EnterpriseCooperation Courses (6 courses):
Introduction to IntelligentTransportation and Digital Construction, Understanding Internship, ProfessionalInternship, Cutting-edge Engineering Design Workshop, Graduation Project
Competitive TeachingCombination Courses (3 courses):
Principles and Procedures ofStructural Analysis, Concepts and Experiments of Structural Models, ModularConstruction of Prefabricated Structures and Engineering Applications
Innovation PracticeCourses (4 courses):
Structural Model Concept andExperiment, Engineering Material Design Experiment, Civil Engineering FrontierTest, Structural Vibration Test Technology and Practice
All-English TaughtCourses (10 courses):
Theoretical Mechanics III.,Mechanics of Materials VI, Engineering Surveying and Mapping and DigitalArchitecture, Structural Mechanics, Theory of Concrete Structures, Theory ofSteel Structures, Elastic Mechanics I, Constructive Design and Construction ofMaterials, Principles and Basis of Structural Analysis Procedures, ElasticMechanics and Finite Element Method
Bachelor-Master SharedCourses (6 courses):
Elastic Mechanics and FiniteElement Method (All-English Taught), 3D Printing Materials and Structures,Intelligent Construction Theory and Methods, Structural Dynamics, HigherReinforced Concrete Structures, European and American Road Engineering Designand Analysis
1. Registration form for various coursecredits
(1) Credit StatisticsTable
Course Categories | Course Requirements: | Credits | Hours | remark | |||||||
Common Basic Courses | Compulsory | 58.5 | 1120 |
| |||||||
General Knowledge | 10 | 160 |
| ||||||||
Fundamentals of the major | compulsory | 33.5 | 592 |
| |||||||
Elective course | Take | 23 | 368 |
| |||||||
Total | 125 | 2240 |
| ||||||||
Intensive hands-on teaching sessions | compulsory | 35 | 41 weeks |
| |||||||
Graduation Credit Requirements | 125.0+35.0=160.0 | ||||||||||
It is recommended to take credits each semester | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||
26.5 | 24 | 26 | 23.5 | 22.5 | 14.5 | 13 | 10 | ||||
Note: Students are required to complete the required creditsof the professional teaching plan upon graduation, and obtain 5 credits ofhumanities quality education and 4 credits of innovation ability training inthe second classroom.
(2) Category statistics table
Hours | Credits | ||||||||||
Total number of credit hours | Therein | Therein | Total number of credits | Therein | Therein | Therein | |||||
Compulsory hours | Elective hours | Theoretical teaching hours | Experimental teaching hours | Compulsory Credits | Elective credits | Credits for the Intensive Practice Teaching Session | Theoretical Teaching Credits | Experimental Teaching Credits | Innovation and Entrepreneurship Education Credits | ||
2240 | 1712 | 528 | 1864 | 376 | 160 | 127 | 33 | 35 | 116.5 | 8.5 | 4 |
Note:
1. General education courses are counted as electives;
2. The experimental teaching hours in thistable include experiments, internships and others in the professionalteaching plan;
3. Innovation and entrepreneurship education credits:The courses in the training plan shall be recognized by the teaching steeringcommittee of each department, including the credits of the combination ofcompetition and education,innovation practice courses, and entrepreneurship education courses;
4. Compulsory hours + elective hours = total number ofhours; Theoretical teaching hours + experimental teaching hours = totalteaching hours; Compulsory Credits + Elective Credits = Total Credits; Concentrated practice teaching link credits +theoretical teaching credits + experimental teaching credits = total credits.
2. Curriculum Schedule
Category | Curriculum code | Course name | Compulsory / Elective | Number of hours | Credits | Commencement of classes semester | ||||
Total credit hours | Theory | Experiment | Exercitation | Other | ||||||
Public Fundamentals | 031101661 | Ideology, morality and the rule of law | C | 40 | 36 |
|
| 4 | 2.5 | 1 |
031101761 | An Introduction to Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a | C | 48 | 36 |
|
| 12 | 3.0 | 2 | |
031101424 | Introduction to Mao Zedong Thought and the Theoretical System of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics | C | 40 | 36 |
|
| 4 | 2.5 | 3 | |
031101522 | Basic Principles of Marxism | C | 40 | 36 |
|
| 4 | 2.5 | 3 | |
031101371 | Outline of Modern Chinese History | C | 40 | 36 |
|
| 4 | 2.5 | 4 | |
031101331 | Situation and policy | C | 64 | 64 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 1-8 | |
044101383 | English for Academic Purposes I | C | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 1 | |
044102452 | English for Academic Purposes II | C | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 2 | |
084101181 | Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (Science & Engineering) | C | 36 | 24 |
|
| 12 | 2.0 | 2 | |
052100332 | Physical Education I | C | 36 |
|
|
| 36 | 1.0 | 1 | |
052100012 | Physical Education II | C | 36 |
|
|
| 36 | 1.0 | 2 | |
052100842 | Physical Education III | C | 36 |
|
|
| 36 | 1.0 | 3 | |
052100062 | Physical Education IV | C | 36 |
|
|
| 36 | 1.0 | 4 | |
006100112 | Military doctrine | C | 36 | 18 |
|
| 18 | 2.0 | 2 | |
040100051 | Calculus II. (I). | C | 80 | 80 |
|
|
| 5.0 | 1 | |
040100411 | Calculus II. (II). | C | 80 | 80 |
|
|
| 5.0 | 2 | |
040100401 | Linear Algebra and Analytic Geometry | C | 48 | 48 |
|
|
| 3.0 | 1 | |
040100023 | Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics | C | 48 | 48 |
|
|
| 3.0 | 2 | |
041100582 | University Physics I. (I). | C | 48 | 48 |
|
|
| 3.0 | 2 | |
041101391 | University Physics I. (II). | C | 48 | 48 |
|
|
| 3.0 | 3 | |
041100671 | University Physics Experiment I | C | 32 |
| 32 |
|
| 1.0 | 3 | |
041101051 | University Physics Experiment II | C | 32 |
| 32 |
|
| 1.0 | 4 | |
037102783 | University Chemistry | C | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 3 | |
037101943 | University Chemistry Experiments | C | 16 |
| 16 |
|
| 0.5 | 4 | |
045102811 | Programming in Python language | C | 40 | 32 |
|
| 8 | 2.0 | 1 | |
074106601 | Fundamentals of Design Expression | C | 64 | 54 | 10 |
|
| 3.0 | 1 | |
| Humanities, Social Sciences | E | 128 | 128 |
|
|
| 8.0 | 1-8 | |
| Science and Technology Field | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 1-8 | ||
total | C | 1280 | 958 | 80 |
| 242 | 68.5 |
| ||
Note: The rest of the class hours can be computer andpractical hours.
2. Curriculum Schedule (continued)
Fundamentals of the major | 033109241 | Introduction to Intelligent Transportation and Digital Construction | C | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 1 | |
033109121 | Theoretical Mechanics III. | Choose 1 out of 2 (English Expansion Option) | C | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 3 | |
033109481 | Theoretical Mechanics III | C | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 3 | ||
033110111 | Mechanics of Materials VI | Choose 1 out of 2 (English Expansion Option) | C | 64 | 58 | 6 |
|
| 3.5 | 3 | |
033110112 | Mechanics of Materials VI (English) | C | 64 | 58 | 6 |
|
| 3.5 | 3 | ||
033109131 | Engineering Surveying & Mapping & Digital Architecture | Choose 1 out of 2 (English Expansion Option) | C | 52 | 40 | 12 |
|
| 3.0 | 3 | |
033109132 | Engineering Surveying and Digital Architecture (English) | C | 52 | 40 | 12 |
|
| 3.0 | 3 | ||
032101653 | Structural mechanics | Choose 1 out of 2 (English Expansion Option) | C | 64 | 64 |
|
|
| 4.0 | 4 | |
032101654 | Structural Mechanics (English) | C | 64 | 64 |
|
|
| 4.0 | 4 | ||
032101622 | hydrodynamics | C | 32 | 28 | 4 |
|
| 1.5 | 4 | ||
033109161 | Engineering Geology & Engineering Materials | C | 66 | 54 | 12 |
|
| 3.5 | 4 | ||
033107692 | Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering | C | 72 | 64 | 8 |
|
| 4.0 | 5 | ||
033101932 | Theory of concrete structures | Choose 1 out of 2 (English Expansion Option) | C | 64 | 64 |
|
|
| 4.0 | 5 | |
033101933 | Theory of Concrete Structures (English) | C | 64 | 64 |
|
|
| 4.0 | 5 | ||
033100861 | Steel Structure Theory | Choose 1 out of 2 (English Expansion Option) | C | 50 | 40 |
|
| 10 | 2.5 | 5 | |
033100862 | Theory of Steel Structures (English) | C | 50 | 40 |
|
| 10 | 2.5 | 5 | ||
033109251 | Principles of Engineering Construction and Cost Management | C | 64 | 62 |
| 2 |
| 3.5 | 6 | ||
total | C | 592 | 538 | 42 | 2 | 10 | 33.5 |
| |||
Major electives | Seminar module for new students (minimum 1.0 credits required). | ||||||||||
033109881 | Smart transportation and sustainable development | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 2 | ||
033109941 | Frontiers of digital design and intelligent construction | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 2 | ||
033109171 | Engineering management in the era of artificial intelligence | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 2 | ||
033109541 | Digital twin watersheds and future water conservancy | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 2 | ||
033109991 | Future urban science: intelligent design and sustainable systems | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 2 | ||
033108751 | New materials, new structures, new engineering: application of mechanical thinking | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 2 | ||
total | E |
|
|
|
|
| 1.0 |
| |||
Elective courses with cutting-edge characteristics (minimum 12 credits, of which at least 6 credits are in the same module). | |||||||||||
033110041 | Green and intelligent design of human settlements | Module 1: High-performance building structures and low-carbon construction | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 4 | |
033110131 | Green building materials and low-carbon construction | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5/6 | ||
033110171 | High performance materials & engineering applications | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033109341 | Prefabricated modular construction and engineering application | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6/7 | ||
033109311 | Intelligent and optimized design of high-rise building structure | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
033109351 | Wind vibration effects and control of megastructures | Module 2: Disaster prevention and mitigation throughout the life cycle of engineering structures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | |
033108722 | Engineering safety accident analysis and emergency response | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5/6 | ||
033110181 | Monitoring technology for the construction process of large and complex structures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5/6 | ||
033110081 | Earthquake prevention and mitigation of engineering structures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033110191 | Fire effect and prevention of building structures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
033109331 | Frontier and practice of new complex structure construction technology | Module 3: Intelligent construction and digital operation and maintenance of engineering structures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | |
033109361 | Structural health monitoring, internet of things and data science | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5/6 | ||
033110061 | Structural intelligent perception and engineering diagnosis | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033110071 | High-performance structural optimization and algorithm design | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033109181 | Urban digital operation and management | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033104272 | Environmental geotechnical engineering | Module 4: Urban marine geotechnical engineering and underground space development | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 4 | |
033109401 | Smart underground space and engineering | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033110201 | Coastal soft foundation treatment and underground space excavation support | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033110051 | Intelligent diagnosis and repair of service performance of underground structures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033109391 | Intelligent rock mass analysis and green underground structure design | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
033109421 | Digital bridge engineering and AI design | Module 5: New technologies for the construction of major transportation infrastructure | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | |
033109321 | Digital construction technology for tunnel engineering | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033109371 | Bridge intelligent inspection technology and machine vision application | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033109381 | A new generation of bridge and tunnel maintenance technology | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033109411 | Evolution of Bridge Structures: Innovative Exploration of Steel and Concrete Combinations | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6/7 | ||
033110121 | Green and resilient road construction and maintenance technology | Module 6: Green and resilient road construction and maintenance integration technology | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 4 | |
033110211 | Future road structures and materials | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033103494 | Road survey design | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5/6 | ||
033110011 | Simulation technology for modern transportation infrastructure | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033110221 | Subgrade and slope design and safety | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
total | choose |
| E |
|
|
| 12.0 |
| |||
General Category Platform Electives (A minimum of 10.0 credits is required, and a maximum of 2 cross-faculty electives are recognized.) 0 credits). | |||||||||||
033109031 | Civil & transportation laboratory safety | Engineering Liberal and Interdisciplinary Literacy module | E | 24 |
| 24 |
|
| 1.0 | 3 | |
033107221 | Ocean-based renewable energy | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 3 | ||
033109711 | Fundamentals of operations research | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 3/4 | ||
033109511 | Design experiments for engineering materials | E | 16 |
| 16 |
|
| 0.5 | 4 | ||
033101571 | Structural model concepts and experiments | E | 22 | 16 | 6 |
|
| 1.0 | 4/6 | ||
033109431 | Elastic mechanics I | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033109491 | Elastic mechanics I (English) | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033108521 | Frontiers of academic and engineering innovation | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 5/6 | ||
033110141 | Structural vibration testing technology and practice | E | 24 | 8 | 16 |
|
| 1 | 5/6 | ||
033110151 | Experiments on engineering structures | E | 32 | 16 | 16 |
|
| 1.5 | 6 | ||
033109461 | Engineering economics I | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033109471 | Engineering regulations & contracts I | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033103104 | Engineering project management I | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033108321 | Development and utilization of marine space | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033106143 | Frontier testing in civil engineering | E | 16 | 8 | 8 |
|
| 0.5 | 6/7 | ||
033107751 | Digital image processing and application | Intelligent technology modules | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 3/4 | |
033107793 | Materials constructed design and construction (English) | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 4 | ||
033109691 | Remote sensing and geo-information systems | E | 36 | 32 | 4 |
|
| 2.0 | 5/6 | ||
033108532 | Principles and fundamentals of structural analysis | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033108533 | Principles and fundamentals of structural analysis procedures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033109441 | Non-destructive testing and intelligent data analysis | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5 | ||
033109142 | Engineering big data analysis and application I | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 5/6 | ||
033108611 | Application of web programming in civil engineering | E | 16 | 16 |
|
|
| 1.0 | 6 | ||
033107701 | Artificial intelligence and machine learning | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 6 | ||
033105922 | Elastic mechanics and finite element method | Bachelor-Master Shared Courses | E | 48 | 48 |
|
|
| 3.0 | 7 | |
033108621 | 3d printing materials and structures | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
033110231 | Theory and method of intelligent construction | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
033102333 | Structural dynamics | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 8 | ||
033105881 | High-grade reinforced concrete structure | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 8 | ||
033108631 | Design and analysis of road engineering in Europe and the United States | E | 32 | 32 |
|
|
| 2.0 | 8 | ||
020100051 | Innovative research training | Innovation and Entrepreneurship Class | E | 32 |
|
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | |
020100041 | Innovative research practice I | E | 32 |
|
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
020100031 | Innovative research practice II | E | 32 |
|
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
020100061 | Entrepreneurial practice | E | 32 |
|
|
|
| 2.0 | 7 | ||
total | E | A minimum of 23 credits is required for the total number of credits taken in all elective courses | |||||||||
Note: The rest of the class hours can be computerand practical hours.
Students apply for conversion intocertain credits for professional elective courses (innovative researchtraining, innovative research practice) according to their own scientificresearch training projects, discipline competitions, published papers, patentsand independent entrepreneurship I, innovative research practice II, entrepreneurship practice and otherinnovation and entrepreneurship courses). The total number of credits for eachstudent's application for major electives shall not exceed 4 credits. Projects and competitions that have been approvedby the university as elective credits will no longer receive innovative creditscorresponding to the second classroom.
3. Concentrate on practical teaching
Curriculum Code | Course name | Compulsory/ Elective | Number of hours | Credits | Commencement of semesters | |
Practice | Teaching | |||||
006100151 | Military skills | C | 2 weeks |
| 2.0 | 1 |
031101551 | Marxist theory and practice | C | 2 weeks |
| 2.0 | 3 |
033101582 | Meet the internship | C | 1 week |
| 1.0 | 3 |
033109191 | Engineering geology practice | C | 2 weeks |
| 2.0 | 3 |
033109221 | Engineering surveying and mapping & digital building practice | C | 2 weeks |
| 2.0 | 4 |
033110241 | Steel structure design practice | C | 2 weeks |
| 2.0 | 5 |
033109281 | Basic engineering design practice | C | 2 weeks |
| 2.0 | 6 |
033109271 | Concrete structural design practice | C | 3 weeks |
| 3.0 | 6 |
033109261 | Principles of engineering construction and cost management practices | C | 3 weeks |
| 3.0 | 7 |
033110251 | Cutting-edge engineering design workshop | C | 3 weeks |
| 3.0 | 7 |
033101883 | Professional internships | C | 3 weeks |
| 3.0 | 7/8 |
033100553 | Graduation project (thesis) (including 2 weeks of internship) | C | 16 weeks |
| 10.0 | 8 |
033110261 | Overseas academic and engineering practice research | E | 1 week |
| 1.0 | 4/6 |
Total | C | 41 weeks |
| 35.0 |
| |
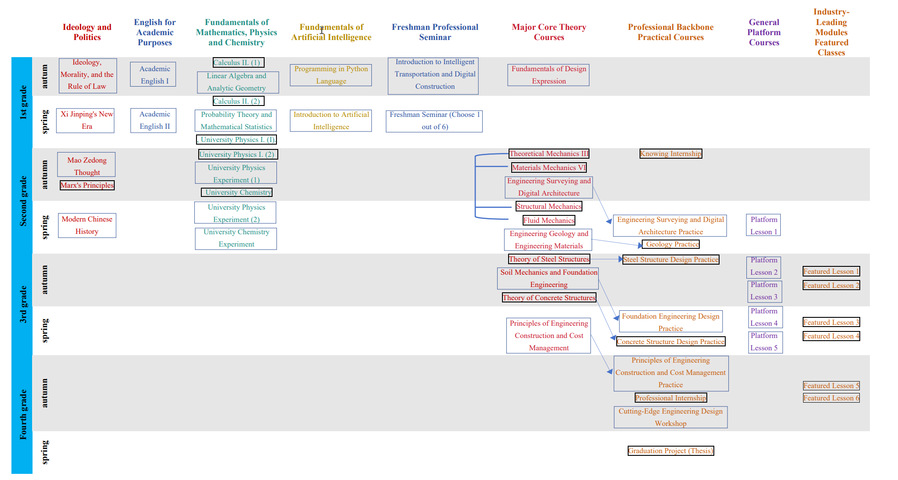
4. Course topology diagram
5.Matrix of the relationship between the curriculum system and graduationrequirements
No. | Course name | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
1 | Ideology, morality and the rule of law | ● |
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
2 | An introduction to Xi Jinping thought on socialism with Chinese characteristics | ● |
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
3 | Outline of modern Chinese history | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
4 | Introduction to Mao Zedong thought and the theoretical system of socialism with Chinese characteristics | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
5 | Basic principles of Marxism | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
6 | Situation and policy | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
7 | English for academic purposes I | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● |
| ● |
8 | English for academic purposes II | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● |
| ● |
9 | Introduction to artificial intelligence (science & engineering) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 | Fundamentals of computer science in college | ● |
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● |
11 | Physical education I | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
12 | Physical education II | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
13 | Physical education III | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
14 | Physical education (4) | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
15 | Military doctrine | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
16 | Calculus II (1) | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 | Calculus II (2) | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 | Linear algebra and analytic geometry | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 | Probability theory and mathematical statistics | ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 | University physics I (1) | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 | University physics I (2) | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22 | University physics experiment I |
| ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 | University physics experiment II |
| ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 | Fundamentals of design expression | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 | Programming in Python language | ● |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 | Introduction to intelligent transportation and digital construction | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
27 | Theoretical mechanics III |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 | Theoretical mechanics III (English) |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 | Mechanics of materials VI |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 | Mechanics of materials VI (English) |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 | Engineering surveying and digital architecture |
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
32 | Engineering surveying and digital architecture (English) |
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
33 | Structural mechanics |
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 | Structural mechanics (English) |
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 | Hydrodynamics |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 | Engineering geology & engineering materials |
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
37 | Soil mechanics and foundation engineering |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 | Theory of concrete structures | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 | Theory of concrete structures | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 | Steel structure theory |
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
| ● |
41 | Steel structure theory (English) |
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
| ● |
42 | Principles of engineering construction and cost management | ● | ● |
|
|
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
43 | Smart transportation and sustainable development | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 | Frontiers of digital design and intelligent construction | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 | Engineering management in the era of artificial intelligence | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 | Digital twin watersheds and future water conservancy | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 | Future urban science: intelligent design and sustainable systems | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 | New materials, new structures, new engineering: application of mechanical thinking | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 | Green building materials and low-carbon construction |
|
|
| ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
50 | Green and intelligent design of human settlements | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 | High performance materials & engineering applications | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52 | Prefabricated modular construction and engineering application |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
53 | Intelligent and optimized design of high-rise building structure | ● | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54 | Monitoring technology for the construction process of large and complex structures |
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
55 | Wind vibration effects and control of megastructures | ● |
| ● |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
56 | Engineering safety accident analysis and emergency response | ● |
| ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
57 | Earthquake prevention and mitigation of engineering structures | ● | ● | ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
58 | Fire effect and prevention of building structures |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59 | Frontier and practice of new complex structure construction technology |
|
| ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 | Structural health monitoring, internet of things and data science |
|
| ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● |
61 | Structural intelligent perception and engineering diagnosis | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
62 | High-performance structural optimization and algorithm design |
| ● |
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
63 | Urban digital operation and management |
| ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64 | Environmental geotechnical engineering | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65 | Smart underground space and engineering |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66 | Coastal soft foundation treatment and underground space excavation support |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
67 | Intelligent diagnosis and repair of service performance of underground structures |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
68 | Intelligent rock mass analysis and green underground structure design |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
69 | Digital bridge engineering and ai design | ● | ● | ● | ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
70 | Digital construction technology for tunnel engineering |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● |
|
|
71 | Evolution of bridge structures: innovative exploration of steel and concrete combinations |
| ● |
| ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
72 | Bridge intelligent inspection technology and machine vision application |
| ● |
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
73 | A new generation of bridge and tunnel maintenance technology | ● |
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
74 | Road survey design |
| ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
|
75 | Green and resilient road construction and maintenance technology |
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
76 | Future road structures and materials |
|
|
| ● | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
77 | Simulation technology for modern transportation infrastructure |
| ● | ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
78 | Subgrade and slope design and safety |
| ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
79 | Civil & transportation laboratory safety | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 | Design experiments for engineering materials |
|
|
| ● |
|
|
|
| ● |
|
|
|
81 | Ocean-based renewable energy | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
82 | Fundamentals of operations research | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
83 | Structural model concepts and experiments |
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
84 | Elastic mechanics I |
| ● | ● |
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
85 | Elastic mechanics I (English) | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
86 | Frontiers of academic and engineering innovation | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
87 | Experiments on engineering structures | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
88 | Engineering economics I | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
89 | Engineering regulations & contracts I | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 | Engineering project management I | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
91 | Development and utilization of marine space | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
92 | Frontier testing in civil engineering |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ● |
| ● |
93 | Structural vibration testing technology and practice | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
94 | Digital image processing and application |
| ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
|
|
|
|
|
95 | Materials constructed design and construction (English) | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
96 | Remote sensing and geo-information system | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
97 | Principles and fundamentals of structural analysis | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
98 | Principles and fundamentals of structural analysis procedures | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
99 | Non-destructive testing and intelligent data analysis |
| ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 | Engineering big data analysis and application I | ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101 | Application of web programming in civil engineering | ● | ● |
| ● |
| ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● |
102 | Artificial intelligence and machine learning |
| ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
103 | Elastic mechanics and finite element method | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104 | 3d printing materials and structures | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
105 | Theory and method of intelligent construction | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
106 | Structural dynamics | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
107 | High-grade reinforced concrete structure | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
108 | Design and analysis of road engineering in Europe and the United States |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
109 | Innovative research training | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
110 | Innovative research practice I | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
111 | Innovative research practice II | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
112 | Entrepreneurial practice | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
113 | Military skills | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
| ● |
|
114 | Marxist theory and practice | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
| ● |
115 | Meet the internship | ● |
| ● |
|
|
| ● | ● |
|
|
|
|
116 | Engineering geology practice | ● |
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
117 | Engineering surveying and mapping & digital building practice | ● |
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
118 | Steel structure design practice | ● |
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
119 | Basic engineering design practice | ● |
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
120 | Concrete structural design practice | ● |
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
121 | Principles of engineering construction and cost management practices | ● |
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
122 | Cutting-edge engineering design workshop | ● |
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
123 | Professional internships | ● |
|
|
|
|
| ● | ● | ● | ● |
|
|
124 | Graduation project (thesis) | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● | ● |
| ● |
125 | Overseas academic and engineering practice research | ● |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. The second class
The second classroom consists of twoparts: humanistic quality education and innovation ability training.
1. Basic requirements for humanisticquality education
Whileobtaining the credits specified in the professional teaching plan, studentsshould also appropriately participate in extracurricular humanistic qualityeducation activities based on their own interests, and the cumulative creditsof participating activities should not be less than 7 credits. Among them, 2credits of mental health education for college students, 1 credit of nationalsecurity education, and 2 credits of career planning for college students areoffered online and included in the second classroom humanistic qualityeducation credits.
2. Basic requirements for thecultivation of innovation ability
Inaddition to obtaining the credits specified in the teaching plan of the major,students must also participate in the National Innovation and EntrepreneurshipTraining Program, the Guangdong Innovation and Entrepreneurship TrainingProgram, the SRP (Student Research Program), the Hundred Step Ladder ClimbingProgram or various extracurricular innovation ability training activities (suchas discipline competitions, academic lectures, etc.) for a certain period oftime, and the cumulative credits of the activities shall not be less than 4credits.
