近日,我系副教授徐大鹏博士以第一作者身份在信息系统领域国际顶级期刊《Information Systems Research》(简称ISR)在线发表了题为“Crowdfunding Success Factors: A Meta-Analytic Investigation”的研究论文。
在线众筹作为一种新兴的融资方式,通过互联网平台连接创业者与投资者,有效解决了传统融资中的信息不对称问题。然而,并非所有众筹项目都能成功,其成功与否受到多种因素的影响。过去的研究从心理学、社会学、管理学、经济学等多个学科视角探讨了众筹成功的驱动因素,但研究结果存在较大分歧,缺乏统一的理论框架。作者通过元分析方法,对173项实证研究进行了系统梳理和定量整合,揭示了影响众筹项目成功的关键因素及其作用机制,为众筹领域的理论和实践提供了重要指导。
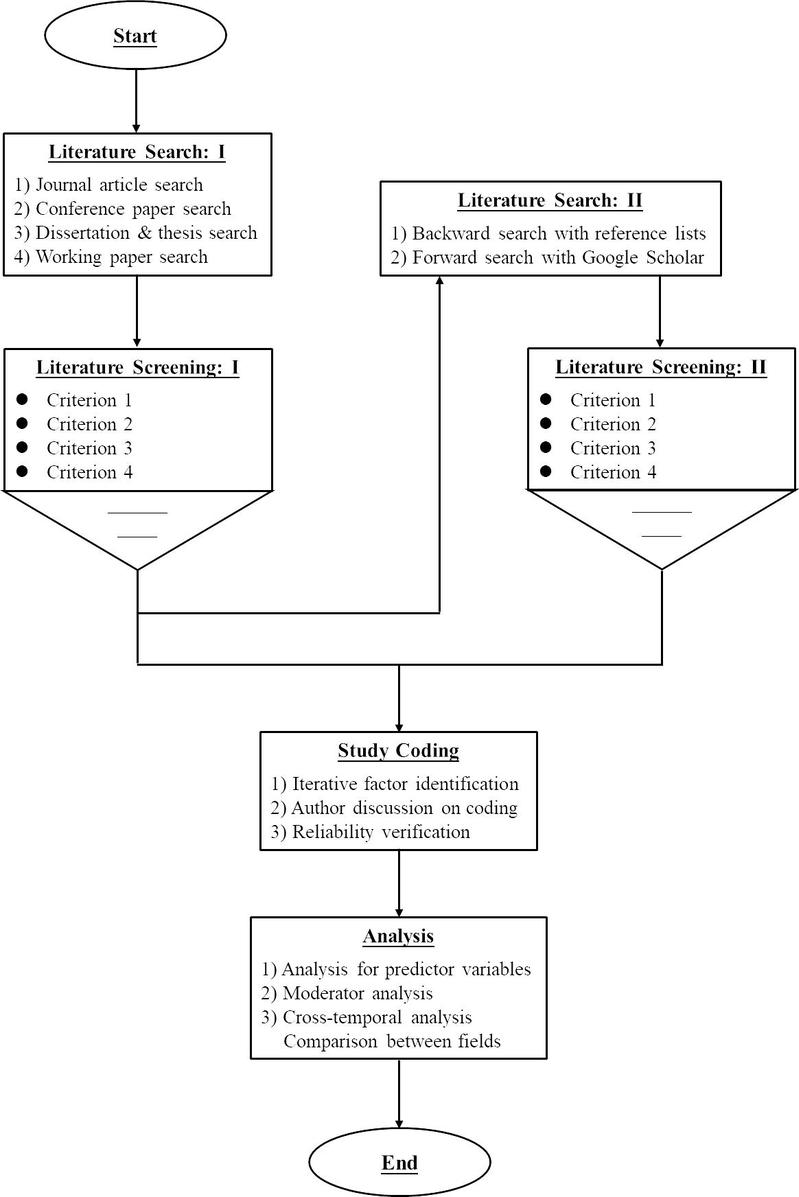
图1 研究流程
研究基于精细加工可能性模型(Elaboration Likelihood Model, ELM),构建了众筹成功因素的综合理论框架。通过元分析技术,将众筹成功因素分为五大类:软信息相关因素(如项目描述质量、外部链接、内部活动等)、筹款人相关因素(如筹款人经验、社会资本等)、支持者相关因素(如早期支持质量)、平台相关因素(如平台推荐)以及项目相关因素(如筹资目标、持续时间等)。研究进一步探讨了众筹成功测量方式、众筹模型、平台知名度和项目所处地区等调节变量对上述关系的影响。
研究发现:软信息相关因素(如高质量的项目描述、积极的社交媒体活动)对众筹成功具有显著正向影响;筹款人相关因素(如社会资本、知识产权)同样对众筹成功起到积极作用;项目相关因素的影响则较为复杂,例如筹资目标与成功呈正相关,而项目持续时间则与成功呈负相关;所提出的调节变量能够显著影响某些成功因素的作用效果。此外,研究还通过横断历史元分析发现,互联网众筹项目的整体成功率随时间呈上升趋势,但增速缺逐渐放缓。
本研究系统整合并扩展了众筹成功因素的理论框架,为后续研究提供了统一的理论基础和工具参考,指明了大量可行方向,有望产生广泛影响。研究不仅拓展了学术研究的边界,也为众筹实践提供了切实可行的指导。研究结果为众筹平台设计个性化推荐系统提供了科学支持,例如基于项目描述质量和发起人信誉的推荐策略优化;也为创业者优化众筹策略(如项目回报结构设计、社交媒体宣传)提供了系统性建议;还为监管部门制定针对众筹平台治理的政策提供了决策支持,助力优化创业生态,进一步激发全社会的创新活力。
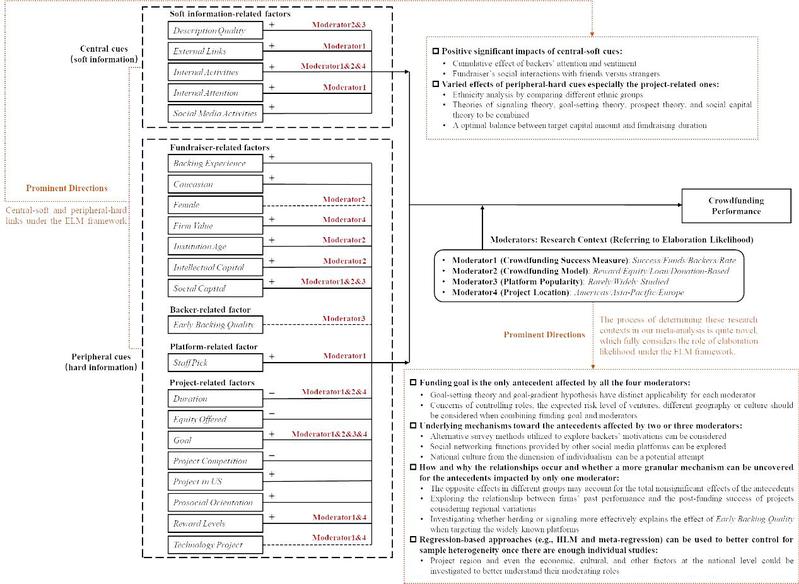
图2 研究理论基础、元分析结论和未来研究方向的综合框架
原文出处
Xu D, Hong H, Deng L, Zhang XM. Crowdfunding Success Factors: A Meta-Analytic Investigation [J/OL]. Information Systems Research, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2022.0640
原文摘要:
A significant body of research has explored various antecedent determinants of crowdfunding success. However, the mixed findings and a lack of theoretical consensus in this domain have impeded efforts to understand which factors truly influence crowdfunding success. In response to this challenge, we carry out a meta-analysis of pertinent research on crowdfunding success factors, guided by elaboration likelihood model (ELM) to construct central and peripheral information links. Drawing upon 173 empirical studies, we categorize all independent variables into 22 widely investigated factors and scrutinize each one’s correlation with crowdfunding performance. Further, we examine the moderating roles of metrics for measuring crowdfunding success, crowdfunding model, platform popularity, and project region in these relationships, which serve as research context factors referring to the role of elaboration likelihood within ELM. In addition, a cross-temporal meta-analysis, using 103 samples, uncovers that while the percentage of successful crowdfunding projects across datasets increases as time goes on, the overall increasing rate slows down over time. Our study synthesizes existing research on the determinants of crowdfunding success, reconciles conflicting results, and pinpoints several reasons for the inconsistencies among existing studies. Our findings facilitate future theoretical developments in this research area and assist market participants in optimizing their practical strategies.
期刊简介
《Information Systems Research》是信息系统领域的国际顶级期刊,由INFORMS(美国运筹学与管理科学学会)出版,致力于发表信息系统与管理科学交叉领域的创新性、高水平研究成果。其研究范畴涵盖了信息系统设计、开发、实施、管理以及应用等多个方面,关注各类信息系统对企业、组织和社会的重要影响。该刊是ABS4*、UTD24、FT50刊物,在国际管理学界享有很高的学术声誉,是全球商学院公认的最高级别学术期刊之一。


