【标题】Application of AgTiO2 in photocatalytic degradation of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether in simulated washing waste containing Triton X-100
【期刊】Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering
【第一作者】 黄开波
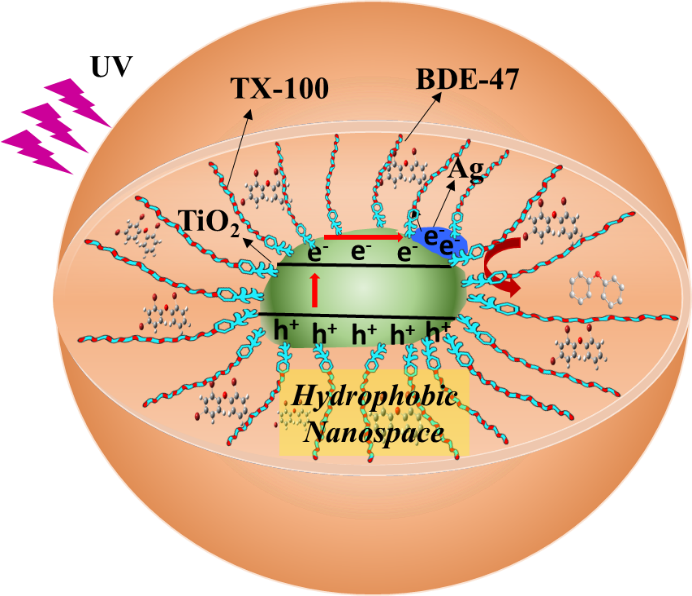
【摘要】Pollution by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) has been a major concern due to their bioaccumulation, persistence, and carcinogenicity. This study aims to use Ag/TiO2 for photocatalytic degradation of PBDEs in washing wastes to reuse Triton X-100 (TX-100) surfactant. The results indicated that Ag/TiO2 accelerated 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) photocatalytic degradation in TX-100 surfactant solutions under anaerobic conditions. When the catalyst is 200 mg/L and the Ag loading is 5%, BDE-47 shown the fastest degradation rate. The adsorption experiments confirmed that BDE-47 adsorption on the photocatalyst or held in micelles depended significantly on the initial concentration of TX-100 (CTX-0). The BDE-47 degradation rate increased first and then decreased with the increasing initial CTX-0 and reached the fastest degradation rate of 0.982 min−1 at 4 CMC. The TX-100 adsorption monolayer on Ag/TiO2 can capture the BDE-47 molecules remarkably well, leading to BDE-47 degradation due to the accumulated electrons on Ag0 in the photocatalysis process. The BDE-47 mainly decays to lower-brominated diphenyl ethers and fewer products accumulated in the Ag/TiO2 system. The loss of TX-100 could be attributed to oxidation by the holes and •OH. The addition of methanol could accelerate the photocatalytic degradation of BDE-47 and decrease the decay of TX-100 during the photocatalysis process. The best methanol dosage is 1%.
【文章链接】https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105077
